Click Below to Order E-book
Click Below to Order Hardcover
Click Below to order Hardcover
*Preface*
The study of history and archaeology offers a window into the past, revealing the evolution of civilizations, cultures, and human achievements. Yet, these fields are rich in specialized terms that often pose a challenge for historians, students, and archaeologists. This Handbook for History and Archaeological Terminology, authored by Lalit Mohan Shukla, seeks to bridge that gap by providing a comprehensive guide to the essential terminology used in both disciplines.
For historians and researchers, this handbook serves as a quick reference, clarifying the nuanced language and concepts that are foundational to their work. It allows them to navigate through complex historical narratives with ease, enhancing their interpretation and analytical skills. Students of history will find this resource invaluable as they grapple with unfamiliar terms during their academic journey. It will not only help them understand these terms in context but also enable them to articulate their own insights with precision and clarity.
Archaeologists, whose work often spans multiple disciplines, will benefit from the clear definitions and explanations of both technical and conceptual terms. Whether in the field or in academic research, understanding the language of archaeology is crucial for interpreting artifacts, site analysis, and historical reconstructions.
In compiling this handbook, great care has been taken to ensure that each term is defined in a way that is accessible yet detailed enough to meet the needs of professionals and scholars alike. As the author, I hope that this resource empowers its readers, enriching their knowledge and contributing to their understanding of history and archaeology.
Lalit Mohan Shukla
B.Sc. , M.A , M.Phil. , [ Ancient Indian History , Culture And Archaeology ] , M.A [ English Literature ] M.Ed.
A
1. *Archaeology*:
The scientific study of the material remains of past human life and activities. Archaeologists excavate sites to uncover artifacts, structures, and other physical evidence to learn about ancient civilizations.
2. *Artifact*:
Any object made, modified, or used by humans, typically an item of cultural or historical interest. Artifacts include tools, pottery, weapons, and jewelry, and are crucial for understanding past societies.
3. *Archaic Period*:
A term used to describe a stage in the development of a culture or civilization, often referring to early phases characterized by hunting, gathering, and rudimentary farming practices. In North American archaeology, it refers to the period roughly 8000 to 1000 BCE.
4. *Ancient History*:
The study of the distant past, from the earliest human civilizations to the early Middle Ages. This period typically covers the time from the beginning of recorded human history around 3000 BCE to the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 CE.
5. *Anthropology*:
The study of humans, their societies, and customs. Anthropology is divided into several subfields, including cultural anthropology, physical anthropology, and archaeological anthropology.
6. *Anachronism*:
An error in chronology in which something is assigned to a time period where it does not belong. In history and archaeology, identifying anachronisms is important to ensure accurate historical interpretation.
7. *Achaeology*:
The study of ancient Greek civilization, including its language, literature, history, and culture. Scholars of Achaeology often focus on the Classical period of Greece.
8. *Assyriology*:
The study of the history, language, and culture of ancient Mesopotamia, primarily focusing on the Assyrian and Babylonian civilizations. Assyriologists decipher cuneiform tablets and study ancient Near Eastern texts.
9. *Atrium*:
A central open area in a building, particularly in Roman houses, which served as a reception hall and living space. The term is also used in archaeology to describe similar architectural features in other ancient structures.
10. *Aeneolithic*:
Also known as the Copper Age, this term refers to a transitional period between the Neolithic (Stone Age) and the Bronze Age, characterized by the first use of copper tools and weapons alongside stone implements.
1. Artifact: An object made or modified by humans, that has historical or archaeological significance. Artifacts can be anything from tools and weapons to pottery and jewelry. They provide clues about the people who made and used them, their culture, and their way of life.
2. Assemblage: A group of artifacts found at an archaeological site that are believed to have been deposited at the same time or by the same people. By studying assemblages, archaeologists can learn about the activities that took place at a site and the types of tools and materials that were used.
3. Archaeoastronomy: The study of how ancient cultures understood and interacted with the celestial bodies. Archaeologists use astronomical alignments of monuments, artifacts, and features to understand how people in the past viewed the cosmos and how it may have influenced their societies.
4. Archive: A collection of historical documents, records, and other materials that are preserved for research purposes. Archives can be found in libraries, museums, and historical societies. They are essential resources for historians and other researchers who want to learn about the past.
5. Absolute Dating: A method of determining the chronological age of an archaeological site, artifact, or other material in years. Unlike relative dating, which only determines the order in which things happened, absolute dating provides a specific date or date range. Common methods of absolute dating include radiocarbon dating and thermoluminescence dating.
6. Aboriginal Title: The legal right of indigenous peoples to their traditional lands and territories. Aboriginal title is a complex issue that has been the subject of much debate and litigation.
7. Acculturation: The process by which one culture comes to resemble another culture, often as a result of contact or conquest. Acculturation can involve changes in language, religion, customs, and other aspects of culture.
8. Archaic Period: A period in human history that falls between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic periods. The Archaic period is characterized by the development of new technologies, such as the bow and arrow, and the beginning of a more settled way of life.
9. Artifact Scatter: A widespread distribution of artifacts across a landscape. Artifact scatters can be the result of hunting and gathering activities, campsites, or battles.
10. Anthropometry: The study of the measurements and proportions of the human body. Anthropometry is used in archaeology to study human evolution, health, and nutrition.
B
1. *Barrow*: A large mound of earth or stones, often covering a burial site, especially from prehistoric times. Common in Europe.
2. *Basilica*: In ancient Rome, a large public building used for legal and civic proceedings, later adapted as a model for Christian churches.
3. *Byzantine Empire*: The continuation of the Roman Empire in the East after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, known for its rich history and contributions to art, law, and architecture.
4. *Bronze Age*: A period in ancient history (approximately 3300-1200 BCE) marked by the use of bronze tools and weapons, preceding the Iron Age.
5. *Battlement*: A defensive parapet with openings or indentations at the top of a wall, used historically in fortifications and castles.
6. *Beaker Culture*: A prehistoric European culture (ca. 2800–1800 BCE) associated with distinctive bell-shaped pottery and often linked to the spread of metalworking.
7. *Babylon*: An ancient Mesopotamian city, significant for its contributions to law (Code of Hammurabi), culture, and architecture (e.g., the Hanging Gardens).
8. *Barbarian*: Historically used by the Romans and Greeks to refer to non-civilized or foreign peoples, often viewed as uncultured or warlike.
9. *Bering Land Bridge*: A land connection between Asia and North America that early humans are believed to have crossed during migration periods.
10. *Burial Mound*: A mound built over a grave or graves, common in prehistoric societies, often signifying status and used for archaeological studies of ancient cultures.
11. *Blockhouse*: A small, fortified building used primarily for defensive purposes, found in various archaeological sites related to military history.
12. *Bastion*: A projecting part of a fortification designed to allow defensive fire in multiple directions, common in medieval and early modern fortresses.
13. *Babylonian Captivity*: The period in Jewish history (597–539 BCE) when many Judeans were exiled to Babylon by Nebuchadnezzar II.
14. *Broch*: A prehistoric, drystone hollow-walled structure found in Scotland, believed to be defensive towers built in the Iron Age.
15. *Balustrade*: A row of small columns topped by a rail, often found in ancient palaces, temples, and fortifications.
16. *Bronze*: An alloy of copper and tin used extensively in tool and weapon making during the Bronze Age, vital to the technological advances of ancient civilizations.
17. *Buttress*: A structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall, commonly seen in ancient Roman and Gothic architecture.
18. *Berserker*: Refers to Norse warriors known for their ferocity in battle, often associated with Viking history and archaeology.
19. *Black Death*: The pandemic that swept through Europe in the 14th century, drastically altering the social and economic fabric of the medieval world, significant in historical studies.
20. *Byre*: A historical term for a barn or shelter for cattle, often found in rural archaeological sites in Europe.
C
1. *Chronology*
The sequential arrangement of events in the order they occurred. Chronology is crucial for historians to understand the timeline of events, eras, and historical periods.
2. *Carbon Dating*
A scientific method used to determine the age of an archaeological find. It measures the decay of carbon-14 in organic materials to estimate when the object was made or used.
3. *Cuneiform*
One of the earliest systems of writing, developed by the ancient Sumerians of Mesopotamia around 3500-3000 BCE. It consists of wedge-shaped marks on clay tablets.
4. *Culture*
Refers to the social behavior, norms, traditions, and collective achievements of human societies. In archaeology, understanding ancient cultures involves studying artifacts, structures, and practices.
5. *Colony*
A territory under the control or influence of another country or empire. Historical colonies, such as those of the Roman or British empires, provide valuable insight into the spread of civilizations.
6. *Citadel*
A fortress typically located on high ground, protecting a city or region. Citadels like the one in Mycenae, Greece, played crucial roles in defense during historical conflicts.
7. *Crusades*
A series of religious wars between Christians and Muslims, mainly fought over the control of the Holy Land between the 11th and 13th centuries. The Crusades shaped medieval history and geopolitics.
8. *Cairn*
A human-made pile or stack of stones, often serving as a marker or memorial. Cairns are found in archaeological sites, particularly in prehistoric burial sites.
9. *Civilization*
A complex society characterized by urban development, social stratification, symbolic communication (like writing), and governance. Ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley are key subjects of archaeological study.
10. *Cemetery*
A designated area for burying the dead. Ancient cemeteries offer valuable archaeological evidence about burial practices, health, and social hierarchy in past cultures.
11. *Celtic*
Refers to the Iron Age peoples who lived in much of Europe, particularly in what is now the British Isles and France. The Celts had distinct languages, art, and religious practices that are studied through archaeological findings.
12. *Ceramics*
Pottery and other objects made from clay that have been hardened by heat. Ceramics are often found at archaeological sites and help researchers understand the culture, trade, and daily life of ancient peoples.
13. *Conquest*
The act of subduing and taking control of a region or territory by force. Historical conquests, such as those by Alexander the Great or the Romans, reshaped the world map and cultural exchanges.
14. *Capstone*
The topmost stone in a structure or monument, particularly in megalithic constructions like Stonehenge. Capstones are key in understanding the engineering capabilities of ancient builders.
15. *Codex*
An ancient manuscript in book form, as opposed to a scroll. Codices were used by civilizations such as the Mayans and Romans, and their preservation has helped historians decode ancient languages and cultures.
16. *Castle*
A fortified structure built during the Middle Ages, typically by nobility or royalty. Castles were centers of defense, governance, and residence, and they provide rich archaeological sites for understanding feudal societies.
17. *Crossbow*
A ranged weapon used historically in warfare and hunting. The invention and use of the crossbow, especially during the Middle Ages, significantly influenced military history.
18. *Coinage*
The system of money or currency, typically in the form of metal coins. Ancient coins found in archaeological digs provide information on trade, economy, rulers, and artistic styles of past civilizations.
19. *Carthage*
An ancient city-state located in modern-day Tunisia. Carthage was a major power in the Mediterranean until its defeat by Rome in the Punic Wars, making it a significant subject in historical and archaeological studies.
20. *Circumvallation*
The construction of a surrounding defensive wall or fortification, often used during sieges. Archaeologists study circumvallation walls to understand military strategies in ancient warfare.
D
1. *Dynasty*
A series of rulers from the same family or lineage, often maintaining power over generations. Famous dynasties, such as the Egyptian Pharaohs or Chinese Ming Dynasty, shaped the political and cultural landscape of their respective regions.
2. *Domestication*
The process by which humans modify the behavior of plants and animals for their benefit, leading to settled agricultural societies. Domestication of crops and animals was a key development in the Neolithic Revolution.
3. *Dig*
Short for "excavation," this refers to the process of carefully uncovering archaeological remains at a site. Digs are essential for uncovering artifacts, structures, and other physical evidence of past human activities.
4. *Deity*
A god or goddess worshipped in ancient civilizations. Many cultures, such as the Greeks, Egyptians, and Mesopotamians, had complex pantheons of deities whose influence is seen in temples, artifacts, and inscriptions.
5. *Debitage*
The waste material produced when shaping stone tools, often found at archaeological sites. Studying debitage helps archaeologists understand ancient tool-making techniques and activities.
6. *Dolmen*
A type of megalithic tomb consisting of two or more vertical stones supporting a horizontal capstone. Dolmens are found in many ancient cultures and provide insights into prehistoric burial practices.
7. *Diorite*
A durable, coarse-grained igneous rock often used by ancient civilizations for creating statues and monuments. Egyptian and Mesopotamian sculptors used diorite to craft high-quality stone artifacts.
8. *Decadence*
Refers to a period of decline or moral decay in a civilization, often associated with the fall of empires like Rome. Decadence is a topic of historical debate as scholars examine the causes of societal collapse.
9. *Dissertation*
An extensive, formal academic document that presents original research, often required for a Ph.D. in history or archaeology. Dissertations contribute new knowledge to the field through detailed analysis and argumentation.
10. *Diaspora*
The dispersion of a people from their original homeland, such as the Jewish Diaspora or the African Diaspora due to the Atlantic slave trade. Archaeologists study material remains from diasporic communities to trace migration patterns and cultural adaptation.
11. *Decipherment*
The process of interpreting and understanding ancient scripts and languages that are no longer in common use. Deciphering hieroglyphs and cuneiform led to breakthroughs in understanding ancient Egyptian and Mesopotamian civilizations.
12. *Dendrochronology*
The scientific method of dating based on the analysis of tree ring patterns. Dendrochronology is used to date wooden structures or objects and helps reconstruct past climate conditions.
13. *Disarticulated*
Refers to the separation of bones from their original anatomical position. In archaeology, disarticulated human or animal remains are studied to understand burial practices, disturbances, or natural decomposition processes.
14. *Doric*
One of the three classical orders of ancient Greek architecture, characterized by simple, heavy columns without a base and a plain capital. Doric columns are a hallmark of Greek temples like the Parthenon.
15. *Drachma*
An ancient silver coin used in Greece and other parts of the Hellenistic world. The discovery of drachmas in archaeological digs helps historians study ancient economies, trade routes, and cultural exchanges.
16. *Doctrine*
A set of beliefs or principles held by a group, often religious or political. Historical doctrines, such as the Doctrine of the Trinity in Christianity or political doctrines in empires, have influenced social and cultural developments.
17. *Dome*
A rounded vault forming the roof of a building or structure, often used in religious or monumental architecture. Domes, such as those in Byzantine and Islamic architecture, represent significant advancements in engineering and design.
18. *Duomo*
An Italian term for a cathedral, often used to refer to the main church in a city. The Florence Duomo, with its iconic dome designed by Brunelleschi, is an architectural and historical landmark.
19. *Deportation*
The forced removal of a population from their homeland, often used in the context of ancient and modern empires. Deportation policies, like those of the Assyrians or during World War II, had significant social and demographic effects.
20. *Drainage System*
The infrastructure used to manage water flow in ancient cities. Advanced drainage systems, such as those found in the Indus Valley Civilization, are studied to understand urban planning, hygiene, and technological development in antiquity.
E
1. *Empire*
A large political unit or state, typically under a single supreme authority, that controls multiple territories or peoples. Notable examples include the Roman, British, and Ottoman Empires, whose rise and fall shaped world history.
2. *Excavation*
The process of digging and uncovering archaeological remains at a site. Excavations reveal artifacts, buildings, and other physical evidence of past civilizations, providing crucial data for historians and archaeologists.
3. *Epigraphy*
The study of inscriptions or engraved texts on materials like stone, metal, or pottery. Epigraphers analyze these inscriptions to understand languages, laws, and historical events from ancient societies.
4. *Eras*
Specific periods in history marked by distinct events, developments, or changes in civilization. Examples include the Victorian Era, the Bronze Age, and the Enlightenment, which are used to categorize human history.
5. *Ethnography*
The scientific description of peoples and cultures with their customs, habits, and mutual differences. In archaeology, ethnography helps to interpret ancient societies by comparing them with contemporary indigenous groups.
6. *Exodus*
The mass departure of a population from one region to another, often due to conflict, disaster, or religious reasons. The biblical Exodus of the Israelites from Egypt is a famous historical and cultural reference.
7. *Effigy*
A sculpture or model of a person, often used in rituals or as a monument. Effigies were commonly made in ancient civilizations for religious or political purposes, such as the effigies of kings and deities.
8. *Egalitarianism*
A principle or belief in human equality, especially in terms of social, political, and economic rights. Egalitarianism has shaped various historical movements and is studied in the context of ancient and modern societies.
9. *Eldership*
A form of governance or leadership in which decisions are made by a council of elders. Many ancient societies, such as those in Africa or Native America, practiced eldership, emphasizing wisdom and experience in leadership.
10. *Enlightenment*
An intellectual movement in 18th-century Europe emphasizing reason, science, and individual rights. The Enlightenment profoundly influenced the development of modern political thought and revolutions, such as the American and French Revolutions.
11. *Epidemic*
A widespread outbreak of a disease that affects a large number of people. Throughout history, epidemics such as the Black Death or smallpox had devastating effects on populations and social structures.
12. *Economy*
The system of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Historians and archaeologists study ancient economies by examining trade networks, currency, and labor systems of past civilizations.
13. *Exile*
The forced removal or voluntary departure of an individual or group from their native land, often for political reasons. Exile has been a common punishment in ancient and modern history, affecting leaders like Napoleon and political dissidents.
14. *Etruscans*
An ancient civilization that lived in what is now modern-day Italy before the rise of Rome. The Etruscans had a significant influence on Roman culture, especially in art, religion, and architecture.
15. *Erosion*
The process by which natural forces like wind, water, or ice wear down the surface of the Earth. Erosion can both reveal and destroy archaeological sites, making it a critical factor in the preservation of historical landscapes.
16. *Elites*
A small group of people with a disproportionate amount of power, wealth, or privilege in a society. Throughout history, elites have often controlled resources, governance, and cultural production, shaping the course of events.
17. *Excommunication*
The official exclusion of a person from participating in the sacraments and services of the Christian Church. This practice, especially in medieval Europe, was a powerful tool of social and political control.
18. *Edict*
A formal proclamation or command issued by a ruler or government. Famous historical edicts, such as the Edict of Milan, which legalized Christianity in the Roman Empire, had far-reaching consequences.
19. *Embargo*
A government order restricting trade or commerce with a particular country. Embargoes have been used throughout history as a form of economic warfare or political pressure, such as the U.S. embargo on Cuba.
20. *Evolution*
The process by which species undergo gradual development and change over time. In archaeology, human evolution is studied through fossil records and ancient tools to trace the development of early hominids into modern humans.
F
1. *Fossil*
The preserved remains or traces of organisms from the distant past, often found in sedimentary rocks. Fossils provide essential information about prehistoric life and are crucial for understanding human evolution.
2. *Feudalism*
A social and economic system prevalent in medieval Europe, where land was owned by lords who allowed vassals to work it in exchange for military service or labor. Feudalism shaped much of European history during the Middle Ages.
3. *Forum*
In ancient Roman cities, the forum was a public space for commerce, politics, and social activities. Archaeological remains of forums offer insights into Roman urban planning and social structure.
4. *Frieze*
A decorative horizontal band found on buildings, often carved or painted. Friezes are commonly seen in classical Greek and Roman architecture, depicting mythological scenes, battles, or processions.
5. *Fortification*
A military structure built for defense, such as walls, towers, and moats. Throughout history, fortifications have been vital for protecting cities, castles, and territories from invasion.
6. *Flint*
A type of hard sedimentary rock often used to create tools and weapons in prehistoric times. Flint artifacts provide key evidence of early human technology and survival strategies.
7. *Faience*
A type of glazed ceramic material used in ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia for making beads, amulets, and small statues. Faience objects are often found in tombs and temples, offering clues about ancient craftsmanship.
8. *Fresco*
A painting technique where pigments are applied directly onto freshly laid plaster. Frescoes are commonly found in ancient Roman, Greek, and Renaissance art and have been uncovered in archaeological sites like Pompeii.
9. *Fief*
In feudal systems, a fief was a piece of land granted by a lord to a vassal in exchange for loyalty and service. Fiefs were the basic economic units in medieval Europe, and their study helps understand land ownership and governance.
10. *Frankincense*
A fragrant resin used in ancient religious ceremonies, particularly in Egypt, Greece, and Rome. Archaeologists often find frankincense residues in temples and burial sites, providing insights into ancient rituals.
11. *Fragment*
A small piece or portion of an artifact, structure, or text. In archaeology, fragments of pottery, sculptures, or manuscripts are often pieced together to reconstruct historical objects or narratives.
12. *Fertile Crescent*
A region in the Middle East known for its rich soil and early agricultural development. The Fertile Crescent is often called the "cradle of civilization" because it was home to early human settlements like Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt.
13. *Folklore*
Traditional stories, myths, and legends passed down orally through generations. Folklore provides valuable cultural context for historians studying the beliefs, practices, and values of ancient and indigenous societies.
14. *Funerary Rites*
Rituals and ceremonies performed in connection with the burial or cremation of the dead. Archaeological evidence of funerary rites, such as tombs and grave goods, helps researchers understand beliefs about the afterlife.
15. *Fluvial*
Referring to processes or landforms created by rivers and streams. In archaeology, fluvial deposits can preserve artifacts and fossils, revealing information about ancient environments and human settlements near water sources.
16. *Facade*
The front or face of a building, often elaborately decorated. Historical facades, such as those in ancient Greek and Roman temples, are studied to understand architectural styles and aesthetic priorities of past civilizations.
17. *Fresco Secco*
A variant of fresco painting where pigments are applied to dry plaster, rather than wet. Though less durable than true frescoes, fresco secco paintings provide insight into decorative art in ancient and Renaissance times.
18. *Fibula*
A brooch or pin used in ancient times to fasten garments. Fibulae are often found in graves and archaeological sites, offering evidence of clothing, fashion, and metalworking techniques of early civilizations.
19. *Forum Romanum*
The central public square in ancient Rome, which served as a hub for political, legal, religious, and commercial activities. Excavations at the Forum Romanum reveal the layout of Roman urban life and governance.
20. *Fieldwork*
The practical work conducted by archaeologists during excavations or surveys. Fieldwork involves collecting data from sites, artifacts, and landscapes, making it fundamental to both archaeology and historical research.
G
1. *Gladiator*
A combatant in ancient Rome who fought in arenas for public entertainment. Gladiators were often slaves or prisoners, and their battles, sometimes to the death, were central to Roman culture and politics.
2. *Grave Goods*
Items buried alongside a deceased individual, often to accompany them in the afterlife. These artifacts, which include pottery, weapons, and jewelry, provide insight into the beliefs, wealth, and social status of ancient societies.
3. *Garrison*
A group of soldiers stationed in a fort or town to defend it. Historical garrisons were essential for the protection and control of territories, particularly in empires like the Romans or the British.
4. *Glyph*
A symbolic figure or character, often used in ancient writing systems. For example, Mayan hieroglyphs were used to record religious, historical, and astronomical information, aiding archaeologists in interpreting ancient texts.
5. *Geoglyph*
Large designs or motifs created on the ground, typically by removing the top layer of soil or arranging stones. The Nazca Lines in Peru are famous examples, and these features often had ceremonial or religious significance.
6. *Guild*
A medieval association of craftsmen or merchants who controlled the practice of their trade. Guilds regulated production, prices, and the quality of goods, playing a major role in the economies of European cities during the Middle Ages.
7. *Gazetteer*
A geographical dictionary or directory used by historians to understand the locations, cities, and places mentioned in ancient texts. Gazetteers are valuable tools for tracing historical sites and regions.
8. *Gaul*
A region of Western Europe during the Roman Empire, inhabited by the Gauls, a Celtic people. Julius Caesar’s conquest of Gaul was a key event in the expansion of Roman territory and is well-documented in historical and archaeological sources.
9. *Griffin*
A mythical creature with the body of a lion and the head and wings of an eagle. In ancient art and architecture, griffins were symbols of strength and protection, often depicted in Greek, Persian, and Roman cultures.
10. *Granary*
A storehouse for grain, essential for the storage and preservation of food supplies in ancient and medieval societies. Archaeologists uncovering granaries provide evidence of agricultural practices and the organization of ancient economies.
11. *Gothic Architecture*
A style of architecture that originated in 12th-century Europe, characterized by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses. Gothic cathedrals like Notre Dame are major historical landmarks that represent the medieval period's cultural and religious priorities.
12. *Glacial Period*
A cold phase in Earth's history when glaciers expanded, often influencing human migration and settlement patterns. Understanding glacial periods helps archaeologists explain changes in early human activity and environmental adaptation.
13. *Garrison Town*
A town built primarily for the accommodation of soldiers. In history, these towns were often strategic military bases, such as York during Roman Britain, that were integral to maintaining control over conquered territories.
14. *Gravestone*
A marker placed at a burial site to commemorate the deceased. Gravestones, especially inscribed ones, provide archaeologists and historians with valuable data on burial practices, language, art, and social structures in past societies.
15. *Gunpowder*
A mixture of chemicals used in firearms and explosives, first invented in China and later spread to Europe. The development and use of gunpowder revolutionized warfare and played a significant role in shaping world history.
16. *Golden Age*
A term used to describe a period of peace, prosperity, and cultural achievements in a civilization. Examples include the Golden Age of Greece under Pericles or the Islamic Golden Age during the Abbasid Caliphate.
17. *Guildhall*
A building used as a meeting place for a guild or municipal authorities. Guildhalls were centers of power and commerce in medieval towns, and their architecture provides insights into the social and political organization of the time.
18. *Gravimetric Survey*
A method in archaeology used to measure variations in the Earth's gravitational field to locate subsurface features such as buried structures or voids. Gravimetric surveys are non-invasive techniques used to identify potential excavation sites.
19. *Gauntlet*
A piece of armor covering the hand, often used by knights and soldiers during the Middle Ages. Gauntlets are frequently found in historical battle sites, providing evidence of medieval warfare and armor technology.
20. *Glyphic Script*
A writing system that uses pictorial symbols, such as the ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs or the Mayan glyphic script. The study of glyphic scripts is crucial for understanding the languages and records of early civilizations.
H
2. *Hellenistic Period*
The era between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BCE and the rise of the Roman Empire, marked by the spread of Greek culture across the Mediterranean and into Asia. It is significant for the fusion of Greek, Persian, Egyptian, and Indian cultural elements.
3. *Hieroglyphics*
An ancient Egyptian writing system that used pictorial symbols to represent words and sounds. Hieroglyphs were used for religious texts, monumental inscriptions, and historical records, providing a key source of information for Egyptologists.
4. *Hominid*
Refers to members of the biological family Hominidae, which includes humans, our ancestors, and other great apes. Archaeological studies of early hominids, such as *Homo habilis* and *Homo erectus*, are crucial for understanding human evolution.
5. *Harappan Civilization*
Also known as the *Indus Valley Civilization*, it was one of the world’s earliest urban cultures, located in what is now Pakistan and northwest India. It is renowned for its advanced city planning, drainage systems, and trade networks.
6. *Heritage*
Refers to cultural, historical, and natural resources passed down from previous generations, including monuments, artifacts, traditions, and landscapes. Heritage conservation is essential for preserving these resources for future generations.
7. *Hypogeum*
An underground burial chamber or temple, commonly found in ancient Mediterranean civilizations. Hypogea were often used by the Romans, Etruscans, and Egyptians, and provide archaeologists with information on funerary practices.
8. *Hoards*
Collections of valuable objects or coins that were deliberately buried or hidden, often during times of war or crisis. Archaeological finds of hoards provide insights into the economic practices, trade, and wealth distribution of ancient societies.
9. *Historiography*
The study of how history is written, including the methodologies and interpretations used by historians over time. Historiography examines how historical narratives have evolved and the biases that may influence them.
10. *Hunter-Gatherers*
Early human societies that relied on hunting animals and gathering wild plants for sustenance, before the development of agriculture. The study of hunter-gatherer societies helps archaeologists understand human subsistence strategies and migration patterns.
11. *Hallstatt Culture*
A prehistoric culture in Central Europe during the early Iron Age, known for its rich burial sites and trade networks. The Hallstatt Culture was significant for the development of early European societies and the spread of iron technology.
12. *Hoarding Site*
A location where large quantities of goods, artifacts, or treasure have been hidden, often discovered in archaeological digs. Such sites can provide valuable insights into the socio-economic conditions of the time.
13. *Hieratic Script*
A cursive form of Egyptian writing used primarily for religious texts and official documents. Hieratic was derived from hieroglyphics and was faster to write, making it common for priests and scribes.
14. *Historical Materialism*
A theory developed by Karl Marx, which posits that material conditions, particularly economic factors, drive historical development and societal change. This theory has influenced the way historians interpret class struggles and social evolution.
15. *Hadrian's Wall*
A defensive fortification in northern England built by the Romans under Emperor Hadrian’s rule around 122 CE. The wall marked the northern boundary of the Roman Empire in Britain and is one of the most significant Roman archaeological sites in the UK.
16. *Halaf Culture*
An early Neolithic culture located in modern-day Syria, Turkey, and Iraq. Known for its pottery, architecture, and the early use of agriculture, the Halaf Culture is important for understanding the development of settled farming communities in the Middle East.
17. *Hierophany*
A manifestation of the sacred or the divine, often associated with religious rituals and locations. Archaeological sites like Stonehenge are often interpreted as places where hierophanies occurred in ancient cultures.
18. *Hypocaust*
An ancient Roman system for underfloor heating, often found in bathhouses and villas. The hypocaust system is an example of the engineering prowess of Roman architecture and provides insights into daily life and luxury in Roman society.
19. *Homestead Act*
A significant piece of U.S. legislation passed in 1862 that allowed citizens to claim public land in the American West. This act played a major role in westward expansion and settlement, and its impact is studied in American history.
20. *Heraldry*
The study of coats of arms and heraldic symbols, often associated with medieval European nobility. Heraldic symbols were used to identify families and individuals in warfare and tournaments, and they offer insights into medieval social structure and identity.
I
1. *Iconography*
The study and interpretation of symbols, images, and visual representations in art and artifacts. Iconography helps historians understand the cultural, religious, and social meanings conveyed through visual media in different societies.
2. *Incunabula*
Refers to books printed before the year 1501, during the early period of the printing press. Incunabula are significant for studying the transition from manuscript to printed books, the spread of literacy, and the dissemination of knowledge in the late Middle Ages and early Renaissance.
3. *Iron Age*
A prehistoric period characterized by the widespread use of iron for tools and weapons, following the Bronze Age. The Iron Age saw significant advancements in technology, agriculture, warfare, and societal organization, influencing the development of various civilizations worldwide.
4. *Isotope Analysis*
A scientific technique used to determine the composition of isotopes in archaeological materials such as bones, ceramics, or metals. Isotope analysis helps trace the geographic origins of materials, understand ancient diets, migration patterns, and environmental conditions during different historical periods.
5. *In situ*
A Latin term meaning "in its original place." In archaeology, artifacts found in situ are preserved in the exact location where they were originally deposited, providing valuable context for interpretation and understanding the spatial relationships within a site.
6. *Intaglio*
A technique of engraving or carving into a material, often used in creating seals, jewelry, or decorative items. Intaglio designs are studied to understand artistic styles, symbolic meanings, and technological capabilities of ancient cultures.
7. *Inca Empire*
The largest empire in pre-Columbian America, centered in modern-day Peru. The Inca Empire is renowned for its advanced engineering, architecture (such as Machu Picchu), extensive road systems, and sophisticated administrative organization, which facilitated control over vast and diverse territories.
8. *Intermediate Period*
A term used to describe transitional phases between major historical periods or civilizations. For example, the Intermediate Periods in Ancient Egypt refer to times of political fragmentation and instability between more unified eras, providing insights into the dynamics of power and societal change.
9. *Interment*
The burial of a body in a grave or tomb. Studying interments provides archaeologists with information about burial practices, social status, health, and cultural beliefs regarding death and the afterlife in different societies.
10. *Inheritance*
The passing of property, titles, and other assets from one generation to the next. In historical studies, inheritance practices reveal social structures, family dynamics, and economic systems, highlighting how wealth and power were transferred and maintained.
11. *Imperialism*
The policy of extending a country's power and influence through colonization, military force, or other means. Studying imperialism helps historians understand the expansion of empires, cultural exchanges, economic exploitation, and conflicts that have shaped global history.
12. *Ivory*
A valuable material derived from the tusks of animals such as elephants, used in art, toolmaking, and trade in many ancient societies. Archaeological findings of ivory objects provide insights into craftsmanship, trade networks, and the economic value placed on certain materials.
13. *Ironworking*
The process of creating tools, weapons, and structures from iron. The development and refinement of ironworking technology had a profound impact on societies, enabling more efficient agriculture, warfare, and construction, and facilitating the growth of civilizations.
14. *Indigenous*
Referring to the original inhabitants of a region or country. Indigenous history and archaeology focus on the cultures, traditions, and material remains of native populations, often addressing issues of colonization, cultural preservation, and the impact of external influences.
15. *Inscription*
Written text carved or engraved on durable materials like stone, metal, or pottery. Inscriptions are critical primary sources for understanding languages, laws, religious practices, and historical events, providing direct evidence of past societies’ communication and record-keeping.
16. *Irrigation*
The artificial application of water to land for agricultural purposes. Studying ancient irrigation systems helps archaeologists understand agricultural practices, settlement patterns, and environmental management, highlighting how civilizations adapted to and modified their environments.
17. *Isotope*
Variants of elements with different numbers of neutrons, used in various scientific analyses. In archaeology, isotopes are utilized in methods like isotope analysis to study diet, migration, and environmental conditions, offering precise data on ancient human activities and ecological contexts.
18. *Iceman*
Refers to exceptionally well-preserved human remains found in ice, such as Ötzi the Iceman from the Alps. Iceman discoveries provide unparalleled insights into ancient lifestyles, health, technologies, clothing, and the environments in which early humans lived, due to the exceptional preservation of organic materials.
19. *Isolation*
The state of being separated from others, which can affect the development of societies. In archaeology, isolation can explain unique cultural traits, limited technological diffusion, and distinct artistic styles, revealing how geographical and social barriers influence cultural evolution.
20. *Iconoclasm*
The deliberate destruction of religious or cultural symbols and icons, often for political or ideological reasons. Studying iconoclasm helps historians understand conflicts, shifts in power, and changes in religious or cultural practices, as well as the motivations behind the eradication of certain symbols.
J
1. *Jade*
A precious stone used by ancient cultures, particularly in East Asia and Mesoamerica, for crafting tools, ornaments, and ritual objects. Jade artifacts provide insights into trade, craftsmanship, and cultural significance within these civilizations.
2. *Jarl*
A title used in Viking society to denote a noble or chieftain. The Jarl class was part of the social hierarchy in Scandinavian history, and their roles in governance, warfare, and society are studied through archaeological finds and historical records.
3. *Jericho*
One of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, located in modern-day Palestine. Jericho is famous for its ancient walls and significant archaeological layers that provide evidence of early urban settlement, agriculture, and social organization.
4. *Jesuit*
A member of the Society of Jesus, a Catholic religious order founded in the 16th century. Jesuits played a significant role in missionary work, education, and cultural exchanges during the Age of Exploration, particularly in Asia, the Americas, and Africa.
5. *Jomon Period*
A prehistoric period in Japan, lasting from around 14,000 BCE to 300 BCE. It is characterized by the production of distinctive cord-patterned pottery, hunter-gatherer societies, and early forms of agriculture, providing key insights into early Japanese history.
6. *Judaism*
One of the oldest monotheistic religions, originating in the ancient Near East. The study of Judaism's history, texts (such as the Torah), and archaeological remains (like ancient synagogues and tombs) offers critical insights into the development of religious traditions, beliefs, and cultural practices.
7. *Julius Caesar*
A Roman general, statesman, and key figure in the transition from the Roman Republic to the Roman Empire. Caesar's conquests, political reforms, and assassination in 44 BCE have left a lasting impact on Roman history, and his legacy is studied extensively in historical and archaeological contexts.
8. *Jomon Pottery*
A type of early pottery from the Jomon Period of Japan, known for its intricate cord-marked patterns. These ceramic artifacts are significant for understanding the early development of pottery-making techniques and the cultural practices of prehistoric Japan.
9. *Judicial System*
The system of courts and legal institutions in ancient and historical societies. Studying ancient judicial systems, such as those of Greece, Rome, or Mesopotamia, provides insights into governance, law enforcement, social justice, and the administration of legal codes.
10. *Jerusalem*
A city of immense historical and religious significance to Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Archaeological excavations in Jerusalem reveal layers of history, from ancient Canaanite settlements to Roman, Byzantine, and Islamic periods, offering a rich record of cultural and religious transformations.
11. *Jar Burial*
An ancient funerary practice in which human remains are placed in large ceramic jars for burial. This method was used by various cultures, including the Ancient Near East and Southeast Asia, and provides information on mortuary customs and social stratification.
12. *Jataka Tales*
A collection of stories about the previous lives of the Buddha, found in Buddhist literature. These tales are important for understanding Buddhist teachings, cultural values, and the spread of Buddhism across Asia.
13. *Jomon Culture*
The term used to describe the prehistoric culture of the Jomon Period in Japan. The Jomon people are known for their early use of pottery, fishing, and hunting-gathering lifestyles, offering important data on early human settlement patterns in East Asia.
14. *Johann Gutenberg*
The inventor of the movable-type printing press in the 15th century. His innovation revolutionized the production of books and dissemination of knowledge, marking the beginning of the print era and greatly influencing the course of European history.
15. *Jamestown*
The first permanent English settlement in North America, founded in 1607 in Virginia. Archaeological digs at Jamestown have uncovered early colonial artifacts, providing insight into the lives of settlers, interactions with Indigenous peoples, and the struggles of early colonization.
16. *Judgment of Paris*
A mythological story from ancient Greece, in which Paris, a prince of Troy, is asked to judge which goddess—Hera, Athena, or Aphrodite—is the most beautiful. The Judgment of Paris is often depicted in ancient art and has been studied for its influence on the narrative of the Trojan War.
17. *Jizyah*
A tax levied on non-Muslims in Islamic empires, particularly during the medieval period. The collection and administration of the jizyah tax are studied to understand the relationships between Muslim rulers and their non-Muslim subjects, as well as the economic and social dynamics of Islamic states.
18. *Julian Calendar*
Introduced by Julius Caesar in 45 BCE, the Julian Calendar was used throughout the Roman Empire and remained in use in Europe until the adoption of the Gregorian Calendar in 1582. The calendar’s structure and its impact on timekeeping and religious observances are important topics in historical studies.
19. *Judicature*
The administration of justice in historical societies, including courts, judges, and legal procedures. The study of ancient judicatures, such as those in Rome or medieval Europe, provides insights into the development of legal systems, governance, and social order.
20. *Jihad*
An Islamic term meaning "struggle" or "effort," often interpreted as both a personal spiritual struggle and, in some contexts, a military effort to defend Islam. The concept of jihad has played a significant role in Islamic history, influencing political and military developments throughout various periods.
K
1. *Kurgan*
A type of burial mound or tumulus commonly associated with early nomadic cultures in the Eurasian steppes, particularly the Scythians and other Indo-European groups. Kurgans are often rich in grave goods and provide significant insights into the social and ritual practices of these ancient cultures.
2. *Knossos*
An ancient Minoan city on the island of Crete, famous for its large palace complex. Excavations at Knossos have revealed significant information about Minoan civilization, including art, architecture, and early forms of writing like Linear A and Linear B.
3. *Kerameikos*
The potters’ quarter of ancient Athens, also home to a large cemetery. The site is important for the study of Greek funerary practices and pottery production, and numerous artifacts found here have contributed to understanding Athenian life and culture.
4. *Khmer Empire*
A powerful Southeast Asian empire that flourished from the 9th to the 15th centuries, known for its monumental temple complexes like Angkor Wat. Archaeological studies of the Khmer Empire have uncovered its advanced urban planning, architecture, and hydraulic engineering.
5. *Koine Greek*
A common form of the Greek language that developed after the conquests of Alexander the Great and was widely spoken across the Hellenistic world. Koine Greek is particularly significant for its use in early Christian texts and the New Testament.
6. *Kiln*
A high-temperature oven used for firing pottery, bricks, and other materials. The discovery of ancient kilns provides evidence of technological advancements in ceramics, construction, and metallurgy, helping archaeologists understand the industrial and artistic capabilities of past societies.
7. *Kushite Dynasty*
A series of kings from the Kingdom of Kush (in modern-day Sudan) who ruled over Egypt during the 25th Dynasty (circa 744–656 BCE). The Kushite rulers, also known as the "Black Pharaohs," are known for reviving many traditional Egyptian practices and contributing to Egyptian cultural and architectural development.
8. *Knapping*
The process of shaping stone tools through the controlled removal of flakes from a larger piece of stone, typically flint or obsidian. The study of knapping techniques in archaeology helps researchers understand tool-making practices of prehistoric peoples.
9. *Kofun*
A type of large burial mound used in Japan during the Kofun period (250–538 CE). The tombs, often shaped like keyholes, were built for members of the elite, and the artifacts found within them provide important information about early Japanese social structures and cultural practices.
10. *Kalyptic Architecture*
Refers to architecture designed with concealed or hidden elements, such as secret rooms or passageways. In historical studies, kalyptic architecture is often examined in religious or defensive structures, providing insights into security practices and spiritual beliefs.
11. *Kurgan Hypothesis*
A theory about the origins of the Indo-European language family, which suggests that the speakers of Proto-Indo-European were originally located in the Pontic-Caspian steppe, and that the spread of the Kurgan culture played a key role in their migration.
12. *Kamares Ware*
A style of Minoan pottery characterized by its vibrant colors and intricate designs, produced during the Middle Minoan period. Kamares ware is an important marker for archaeologists in dating Minoan archaeological layers and understanding the trade and artistic preferences of the time.
13. *Kingdom of Aksum*
An ancient kingdom located in present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea, known for its monumental stelae, the introduction of Christianity, and its role as a major trading empire. The Kingdom of Aksum was one of the most influential states in the region from the 1st to the 7th century CE.
14. *Khirbet*
An Arabic term used in archaeology to refer to ruins or abandoned towns and villages in the Middle East. Khirbet sites often contain remnants of ancient civilizations and are key to understanding the historical landscape of the region.
15. *Keystone*
The central, wedge-shaped stone in an arch that holds the other stones in place. The keystone is a critical element in ancient Roman and Greek architecture and helps archaeologists reconstruct ancient building techniques.
16. *Kamishibai*
A traditional form of Japanese street theater and storytelling using illustrated boards. Though not strictly an archaeological term, kamishibai helps historians understand the cultural storytelling practices in Japan and its influence on modern visual media.
17. *Kyrios*
A Greek term meaning "lord" or "master," often used to describe the head of a household in ancient Greece. Understanding the role of the kyrios in Greek society is important for the study of family dynamics, social hierarchy, and gender roles in ancient Greece.
18. *Kushan Empire*
A historical empire in Central and South Asia that flourished between the 1st and 3rd centuries CE. The Kushan Empire is known for facilitating trade along the Silk Road and for its role in spreading Buddhism, as seen in archaeological findings of Buddhist art and architecture.
19. *Kurgan Stelae*
Stone stelae or carved upright slabs found in kurgans, particularly in the Eurasian steppes. These stelae often depict warriors or symbols and are an important element in understanding the funerary practices and artistic traditions of early nomadic cultures.
20. *Karez*
An ancient underground irrigation system used in arid regions, especially in Persia and Central Asia. The study of karez systems helps archaeologists understand how ancient civilizations managed water resources and sustained agriculture in desert environments.
L
1. *Linear A*
An undeciphered script used by the Minoan civilization of Crete during the Bronze Age (circa 1800–1450 BCE). Linear A is one of the earliest forms of writing in Europe and its study is crucial for understanding Minoan administration and culture.
2. *Linear B*
A script used for writing Mycenaean Greek, the earliest attested form of the Greek language, mainly found on clay tablets. Linear B tablets provide important insights into Mycenaean administration, trade, and religious practices.
3. *Lithic*
A term used in archaeology to describe stone tools or artifacts. Lithic analysis involves studying these tools to understand prehistoric technology, resource use, and cultural development, particularly during the Paleolithic period.
4. *Lapidary*
The art of cutting, engraving, and polishing stones, particularly gemstones. Lapidary work in ancient cultures reveals much about trade, craftsmanship, and aesthetic preferences, as well as the status and wealth of individuals who possessed these items.
5. *Legion*
A unit of the Roman army, consisting of about 4,000 to 6,000 soldiers. Studying the organization, movement, and archaeological remains of Roman legions provides insights into the military, political, and territorial expansion of the Roman Empire.
6. *Lascaux Cave*
A cave in southwestern France famous for its Paleolithic cave paintings, which date to around 17,000 years ago. The paintings, which depict animals and abstract symbols, are a key site for understanding early human art and symbolic behavior.
7. *Latifundium*
A large estate or plantation in ancient Rome, typically worked by slaves. Latifundia were a key element of the Roman economy and social structure, and their study helps explain Roman agricultural practices, land ownership, and wealth distribution.
8. *Lapis Lazuli*
A deep-blue semi-precious stone that was highly valued in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and other cultures for making jewelry, carvings, and inlay work. Lapis lazuli trade routes, particularly from Afghanistan, illustrate the vast trade networks of the ancient world.
9. *Long Barrow*
A type of Neolithic burial monument found mainly in Europe, consisting of an elongated mound of earth and stone. Long barrows were used for communal burials, and their excavation provides valuable information about early agricultural societies and their burial practices.
10. *Lorica Segmentata*
A type of Roman body armor made of overlapping metal strips. The lorica segmentata was worn by Roman soldiers and is often reconstructed from archaeological finds, helping historians understand Roman military equipment and soldiering practices.
11. *Lugal*
A Sumerian term meaning "king" or "ruler." The title of lugal is significant in understanding the governance structures of early Mesopotamian city-states, where kings played central roles in both political and religious life.
12. *Lintel*
A horizontal architectural element that spans an opening, such as a doorway or window. Lintels are often ornately decorated in ancient architecture, and their study helps in the reconstruction of ancient buildings and understanding of structural techniques.
13. *Lydian*
Referring to the ancient kingdom of Lydia, located in what is now western Turkey. The Lydians were notable for being the first people to mint coins, a significant development in economic history, and the study of their coins offers insights into ancient trade and currency systems.
14. *Lapita Culture*
An ancient Pacific Ocean people known for their distinctive pottery, which dates from 1600 to 500 BCE. The Lapita culture is essential to understanding the migration and settlement patterns of Austronesian-speaking peoples across the Pacific islands.
15. *La Tène Culture*
A European Iron Age culture (circa 450–50 BCE) known for its art, weapons, and pottery. The La Tène culture is closely associated with the Celts, and its archaeological remains are key to understanding pre-Roman European societies.
16. *Limes*
A term used in the Roman Empire to denote the border defense system that protected the empire from external threats. The archaeological study of the Roman limes, such as Hadrian’s Wall in Britain, reveals much about Roman military strategy, architecture, and frontier life.
17. *Lithograph*
A method of printing from a stone or metal plate, invented in the 18th century but sometimes used in historical studies to reproduce or study ancient texts and images. Lithographs played a key role in making historical documents and artwork accessible for study.
18. *Lex*
Latin for "law." In Roman history, lex refers to legal codes or statutes passed by the Roman Senate or assemblies. The study of ancient Roman laws, such as the Twelve Tables, provides critical insight into the legal framework of Roman society and its influence on modern legal systems.
19. *Luwians*
An ancient people who lived in what is now western Turkey during the Late Bronze Age. Their language, Luwian, is closely related to Hittite, and Luwian inscriptions and texts are important for understanding the political and cultural landscape of Anatolia during this period.
20. *Libation*
A ritual pouring of a liquid (such as wine or oil) as an offering to a god or spirit, common in many ancient religions. Archaeological evidence of libations, such as vessels and altars, provides insight into religious practices and the role of rituals in ancient societies.
M
1. *Megalith*
Large stone structures or monuments, typically from prehistoric times. Megaliths include stone circles, tombs, and standing stones like Stonehenge. They are important for studying early human engineering, ritual practices, and social organization.
2. *Magna Carta*
A charter of rights agreed to by King John of England in 1215. It is a foundational document in the history of constitutional law and has influenced the development of modern legal and political systems.
3. *Mastaba*
An ancient Egyptian tomb with a flat roof and sloping sides, used during the Early Dynastic Period and Old Kingdom. Mastabas are significant in the development of royal tomb architecture and provide insights into Egyptian burial customs.
4. *Midden*
A refuse heap or mound left by prehistoric people, consisting of shells, animal bones, pottery, and other debris. Middens are crucial for understanding the daily lives, diets, and habits of past societies.
5. *Manuscript*
A hand-written document, particularly important in the study of ancient and medieval history. Manuscripts, such as religious texts or scientific treatises, are invaluable sources of historical knowledge before the advent of printing.
6. *Mesoamerica*
A historical region and cultural area that includes parts of modern-day Mexico and Central America. It was home to several advanced pre-Columbian civilizations, such as the Maya, Aztec, and Olmec, known for their pyramids, writing systems, and astronomical knowledge.
7. *Mesolithic*
The "Middle Stone Age," marking the period between the Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) and the Neolithic (New Stone Age). This era is significant for its technological advancements, including microlithic tools, and the transition from nomadic to sedentary lifestyles.
8. *Mycenaean Civilization*
A Bronze Age civilization on mainland Greece, flourishing between 1600–1100 BCE. Mycenaean archaeology reveals sophisticated palace complexes, Linear B writing, and their role in the legendary Trojan War.
9. *Minoan Civilization*
An advanced Bronze Age civilization on the island of Crete (circa 3000–1100 BCE). Known for their palaces (like Knossos), art, and trade, the Minoans are key to understanding early Mediterranean cultures.
10. *Mortuary Temple*
An Egyptian temple constructed adjacent to a royal tomb, where offerings and rituals for the deceased were performed. Mortuary temples provide valuable information about ancient Egyptian religious practices and beliefs in the afterlife.
11. *Motte-and-Bailey Castle*
A type of fortification with a wooden or stone keep on a raised earthwork (motte) and an enclosed courtyard (bailey). Common in medieval Europe, these castles are significant for understanding feudal defense systems and territorial control.
12. *Mithraism*
A mystery religion centered around the god Mithras, popular among Roman soldiers from the 1st to the 4th centuries CE. Archaeological sites of Mithraic temples (mithraea) provide insights into religious diversity in the Roman Empire.
13. *Mosaic*
A piece of art or decoration made from assembling small pieces of colored stone, glass, or tiles. Mosaics are found in ancient Roman, Byzantine, and Islamic sites, revealing much about artistic practices, religious symbolism, and everyday life.
14. *Magdalenian Culture*
A European Upper Paleolithic culture (17,000–12,000 years ago), known for its advanced tools, art (including cave paintings), and hunting practices. Magdalenian artifacts offer insights into the lives of early Homo sapiens in Ice Age Europe.
15. *Mohenjo-Daro*
One of the largest cities of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization, located in modern-day Pakistan. Its well-planned layout, drainage system, and advanced architecture provide significant insights into urban planning and early civilization in South Asia.
16. *Mosaic Law*
The body of laws given to Moses in the Hebrew Bible, also known as the Torah. These laws have historical significance for understanding ancient religious practices and legal traditions in the Near East and their influence on Western legal systems.
17. *Mausoleum*
A monumental tomb, often constructed for royalty or important figures. The Mausoleum of Halicarnassus, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, is a prime example. Mausoleums reflect ancient architectural grandeur and beliefs about the afterlife.
18. *Magnetometry*
An archaeological surveying technique that measures variations in the Earth's magnetic field caused by buried features or artifacts. It helps locate and map underground structures without excavation, making it crucial for non-invasive archaeology.
19. *Maritime Archaeology*
The study of human interaction with the sea, lakes, and rivers through the excavation of shipwrecks, harbors, and submerged settlements. It provides important insights into trade, warfare, and cultural exchange in ancient and historical societies.
20. *Manorial System*
The economic and social system of medieval Europe, where the lord of the manor exploited the land and labor of peasants. Studying manorial records helps historians understand feudalism, agriculture, and village life in medieval society.
N
1. *Neolithic*
The "New Stone Age," beginning around 10,000 BCE, marked by the transition from nomadic hunting and gathering to settled agriculture. This period saw the domestication of plants and animals, the rise of permanent settlements, and the development of pottery.
2. *Nomadism*
A lifestyle characterized by moving from place to place rather than settling permanently, often following seasonal resources like food and water. Many ancient societies, including pastoralists and hunter-gatherers, practiced nomadism, and studying their migrations helps us understand human adaptation to different environments.
3. *Nabataean Kingdom*
An ancient Arab kingdom, with its capital at Petra (in modern Jordan), known for its advanced hydraulic engineering and monumental architecture. The Nabataeans controlled trade routes and were instrumental in the spice trade between Arabia and the Mediterranean.
4. *Necropolis*
A large, ancient cemetery or burial ground, often associated with major cities or royal tombs. The term is Greek for "city of the dead" and refers to places like the Valley of the Kings in Egypt or the necropolises of ancient Rome.
5. *Numismatics*
The study of coins and currency, which provides valuable information about economic history, trade, iconography, and political changes. Ancient coins help historians and archaeologists trace trade routes, dates of reigns, and shifts in power.
6. *Nubia*
A region along the Nile, located south of Egypt, known for its rich history and interaction with Ancient Egypt. Nubian culture and archaeology provide significant insights into African civilizations, particularly through sites like Meroë and Kerma.
7. *Natufian Culture*
A prehistoric culture in the Levant (circa 12,000–9,500 BCE) that is considered transitional between hunter-gatherer societies and the development of agriculture. Natufian sites reveal early sedentary lifestyles and the first steps toward plant cultivation.
8. *Narthex*
The entrance or lobby area located at the western end of a Christian basilica or church, serving as a space for penitents or those not yet baptized. The architectural study of narthexes sheds light on early Christian worship practices and church design.
9. *Norse*
Refers to the people, culture, and language of Scandinavia during the Viking Age (circa 800–1100 CE). Norse history and archaeology, especially through ship burials and settlements like those in Greenland and Iceland, provide insights into seafaring, trade, and exploration.
10. *Neo-Assyrian Empire*
A major Mesopotamian empire (911–609 BCE) that expanded across the Near East. The empire’s archaeological sites, such as Nineveh and Nimrud, reveal much about Assyrian warfare, administration, and monumental architecture.
11. *Nazca Lines*
Large geoglyphs etched into the desert sands of southern Peru, created by the Nazca civilization between 500 BCE and 500 CE. These lines form patterns and figures, and their purpose, possibly linked to religious or astronomical practices, continues to intrigue archaeologists.
12. *Nart Mythology*
A body of ancient folklore and epic traditions from the Caucasus region, particularly among the Ossetians, Circassians, and other groups. These myths, which tell of legendary heroes (Narts), are significant in understanding the oral traditions and cultural values of these peoples.
13. *Naveta*
A type of megalithic tomb unique to the Balearic Islands, particularly Menorca, dating from the Bronze Age. These boat-shaped tombs reflect early burial practices and social organization in Mediterranean prehistory.
14. *Nabataean Script*
The script used by the Nabataeans to write their version of the Aramaic language. The script is significant for its development into the Arabic script, linking Nabataean culture to the broader history of writing in the ancient Near East.
15. *New Kingdom*
A period in ancient Egyptian history (circa 1550–1070 BCE) known for its wealth, power, and expansive empire-building, with pharaohs like Ramses II and Tutankhamun. Archaeological finds from this era, including temples and tombs, are key to understanding Egypt's zenith.
16. *Nag Hammadi Library*
A collection of early Christian and Gnostic texts discovered in Upper Egypt in 1945. These manuscripts are crucial for understanding early Christian theology and the diversity of beliefs in the early Christian era.
17. *Niaux Cave*
A cave in southern France that contains Upper Paleolithic cave paintings, dating back to around 17,000 BCE. These depictions of animals provide key insights into prehistoric art and symbolic thought.
18. *Nalanda*
An ancient center of learning in Bihar, India, active from the 5th century to the 12th century CE. Nalanda was one of the first residential universities in the world and played a pivotal role in the development of Buddhist scholarship.
19. *Neo-Babylonian Empire*
A Mesopotamian empire (626–539 BCE) that saw the rebuilding of Babylon, including the famed Hanging Gardens and the Ishtar Gate. The empire's history is crucial for understanding the last great phase of Mesopotamian civilization before the Persian conquest.
20. *Neanderthal*
An extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Europe and parts of Asia until around 40,000 years ago. The study of Neanderthal fossils and tools provides key insights into human evolution, particularly regarding their interactions with early Homo sapiens.
O
1. *Obelisk*
A tall, four-sided monument that tapers to a pyramidion at the top. Obelisks were significant in ancient Egypt, where they were often placed at the entrances of temples as symbols of the sun god Ra.
2. *Ostraca*
Pieces of broken pottery or limestone used as writing surfaces in ancient Egypt and Greece. These fragments often contain inscriptions, such as receipts, official orders, or personal messages, providing valuable insights into daily life and administration.
3. *Oasis*
A fertile area in a desert where water is available from underground springs or other sources. Historically, oases have been crucial for trade and settlement in arid regions, like along the Silk Road or in the Sahara Desert.
4. *Oral Tradition*
The passing of knowledge, culture, and history through spoken word, stories, songs, or other forms of oral communication. Oral traditions are critical for understanding societies without written records, such as many indigenous cultures.
5. *Ox-hide Ingots*
Large metal ingots shaped like an ox-hide, used in the Bronze Age Mediterranean as a form of standardized trade currency. These copper ingots were important for the study of ancient trade networks and metallurgy.
6. *Oligarchy*
A form of government where power is held by a small group of individuals or families. Oligarchies were common in ancient Greece, particularly in city-states like Sparta, and studying them helps in understanding political organization in ancient times.
7. *Oracle*
A priest or priestess who acted as a medium through whom gods were believed to communicate. Oracles, such as the Oracle of Delphi in ancient Greece, played a significant role in decision-making processes in religion, politics, and warfare.
8. *Ostrogothic Kingdom*
A Germanic kingdom established in Italy after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century CE. The kingdom is important for the study of the transition between the Roman and Medieval periods in Europe.
9. *Oldowan*
The earliest known stone tool industry, dating to about 2.6 million years ago, associated with early hominins in East Africa. Oldowan tools represent the beginning of human technological development.
10. *Orichalcum*
A legendary metal mentioned in ancient texts, particularly by Plato in his description of Atlantis. While the existence of orichalcum is debated, the term has been used to describe copper-zinc alloys found in some archaeological sites.
11. *Oligocene*
A geological epoch that occurred between 34 and 23 million years ago, important for the study of early primate evolution. Fossils from this period provide insights into the ancestors of modern humans and other primates.
12. *Ogham*
An early medieval alphabet used primarily to write the early Irish language. Ogham inscriptions, found on standing stones in Ireland and Britain, offer important clues about early Celtic languages and communication.
13. *Oppidum*
A large fortified Iron Age settlement, often associated with Celtic tribes in Europe. Oppida were centers of trade, defense, and governance, and their study provides valuable information about pre-Roman societies in Europe.
14. *Oasis Theory*
A theory in archaeology suggesting that the domestication of plants and animals began in oases during periods of drought. This theory is one explanation for the origins of agriculture in the Near East during the Neolithic period.
15. *Octavian (Augustus)*
The first Roman emperor, originally known as Octavian before taking the title Augustus. His reign marked the transition from the Roman Republic to the Roman Empire, a significant era in world history.
16. *Oxus Civilization*
Also known as the Bactria-Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC), this civilization thrived in Central Asia during the Bronze Age. The Oxus Civilization is important for understanding the development of urbanization, trade, and culture in Central Asia.
17. *Orthostat*
A large stone slab set upright, often used as a wall lining in ancient structures. Orthostats are commonly found in Assyrian and Hittite architecture, where they were often carved with decorative reliefs.
18. *Ossuary*
A container or room used to hold the bones of the dead. Ossuaries were used in various cultures, such as in ancient Israel, and are significant in the study of burial practices and beliefs about the afterlife.
19. *Out of Africa Theory*
The most widely accepted theory of modern human origins, proposing that Homo sapiens first evolved in Africa and then dispersed to other parts of the world. This theory is supported by fossil evidence and genetic studies.
20. *Oinochoe*
A type of ancient Greek jug used for pouring wine. Oinochoai were often decorated with scenes from mythology or daily life, and their study helps archaeologists understand ancient Greek social practices and art.
P
1. *Paleolithic*
The "Old Stone Age," a prehistoric period that spans from about 2.5 million years ago to around 10,000 BCE. It is characterized by the use of rudimentary stone tools by early humans and is significant for understanding the evolution of human behavior and technology.
2. *Pantheon*
Refers both to the gods collectively worshiped in a particular religion and to the famous Roman temple built to honor the gods. The concept of a pantheon is key to studying the religious systems of ancient civilizations such as the Greeks, Romans, and Egyptians.
3. *Papyrology*
The study of ancient papyrus manuscripts, mainly from Egypt and the Mediterranean world. These documents, which include texts on law, medicine, literature, and personal letters, provide critical insights into the social, political, and economic life of ancient societies.
4. *Parthenon*
A temple on the Acropolis of Athens dedicated to the goddess Athena. Built in the 5th century BCE, the Parthenon is a symbol of Ancient Greek civilization and is significant in the study of ancient architecture, religion, and politics.
5. *Petroglyph*
Rock carvings or engravings created by prehistoric peoples. Found worldwide, petroglyphs are important archaeological evidence of early human communication, art, and spiritual beliefs.
6. *Phoenicians*
An ancient Semitic-speaking people known for their seafaring skills and the establishment of trade networks across the Mediterranean. The Phoenicians are particularly important for their invention of an alphabetic script, which greatly influenced modern writing systems.
7. *Pleistocene*
A geological epoch that lasted from about 2.6 million to 11,700 years ago, marked by repeated glaciations. It is crucial in archaeology for studying early human evolution, migration patterns, and the development of early tools and cultures.
8. *Pompeii*
An ancient Roman city that was buried by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 CE. The preserved ruins of Pompeii offer a unique snapshot of Roman daily life, architecture, and urban planning in the 1st century CE.
9. *Prehistory*
The period of human history before written records. Archaeologists study prehistory through material remains such as tools, pottery, and art, making it essential for understanding early human societies.
10. *Pyramid*
Monumental structures, particularly associated with ancient Egypt, where they served as royal tombs. Pyramids like those at Giza are critical for understanding ancient Egyptian beliefs about death, the afterlife, and the power of the pharaohs.
11. *Peristyle*
A row of columns surrounding a space within a building, such as a garden or courtyard, especially in Greek and Roman architecture. The design of peristyles reflects the architectural styles and social functions of ancient homes and public buildings.
12. *Polis*
A city-state in ancient Greece, which was the central political unit in Greek society. The study of poleis (plural) is fundamental to understanding the political, social, and cultural development of ancient Greece.
13. *Posthole*
A feature in the ground indicating where wooden posts once stood. Postholes are important in archaeology for reconstructing ancient structures, such as houses or fences, from societies that used wood rather than stone.
14. *Provenance*
The origin or earliest known history of an archaeological artifact or historical object. Establishing provenance is crucial for understanding the context in which an object was made, used, and eventually discovered.
15. *Ptolemaic Dynasty*
The dynasty that ruled Egypt from the death of Alexander the Great (323 BCE) until the Roman conquest (30 BCE). The Ptolemies were of Greek origin and blended Egyptian and Greek culture, playing a significant role in the Hellenistic world.
16. *Petra*
An archaeological site in Jordan, once the capital of the Nabataean Kingdom. Petra is famous for its rock-cut architecture and water conduit system, offering valuable insights into ancient engineering and urban planning in desert environments.
17. *Paleoanthropology*
The scientific study of human evolution through fossils and artifacts. Paleoanthropologists investigate how early humans lived, developed, and spread across the globe, making it crucial for understanding the origins of modern humans.
18. *Papyrus*
A plant-based material used for writing in ancient Egypt, Greece, and Rome. The preservation of papyrus scrolls has provided historians with invaluable documents on religion, governance, law, and everyday life in antiquity.
19. *Permafrost*
A thick layer of soil that remains frozen throughout the year, often preserving organic material such as mammoth bones and early human artifacts. Archaeologists study permafrost in regions like Siberia and Alaska for clues about ancient environments and species.
20. *Pottery*
Ceramic vessels and objects made by ancient peoples, which serve as some of the most common and durable artifacts in archaeology. Pottery shards help researchers date sites, understand trade networks, and reconstruct daily life in ancient societies.
These terms are widely used in *history and archaeology*, and each provides a unique insight into ancient cultures, material remains, and the study of early human civilization.
Q
1. *Quern*
A simple stone tool used for grinding grains into flour. Querns are often found at archaeological sites and provide insights into ancient agricultural practices and domestic life.
2. *Quipu*
A system of knotted strings used by the Inca civilization for record-keeping and communication. Quipus played a significant role in managing the Inca Empire's economy and administration in the absence of a written script.
3. *Quaternary Period*
The most recent geological period, spanning from 2.6 million years ago to the present. It includes the Pleistocene and Holocene epochs and is critical for studying human evolution, glaciations, and environmental changes.
4. *Queen Regent*
A queen who rules on behalf of a child king or when the throne is vacant. Historical examples include Queen Isabella of Spain and Catherine de' Medici of France, whose regencies shaped their nations' political landscapes.
5. *Quaternary Glaciation*
A series of ice ages during the Quaternary Period. The study of these glaciations is important for understanding human migration, adaptation, and the environmental challenges faced by early humans.
6. *Quadriga*
A four-horse chariot used in ancient Rome, especially in races and triumphal processions. Quadrigas are often depicted in Roman art and coins, symbolizing military victory and power.
7. *Quarry*
A site where stone or other materials were extracted for construction. Many ancient structures, such as the Egyptian pyramids and Greek temples, were built using stone from quarries, providing insights into ancient engineering and labor.
8. *Qanat*
An underground water channel used in ancient Persia and other arid regions for irrigation. The qanat system is an important example of ancient water management techniques that enabled agriculture in dry climates.
9. *Quinquereme*
A type of ancient warship used by the Romans, Carthaginians, and Greeks, with five rows of oars. Quinqueremes were a key factor in naval battles during the Punic Wars and other Mediterranean conflicts.
10. *Quarantine*
The isolation of people or goods to prevent the spread of disease. Quarantine practices date back to the Middle Ages and were used to control outbreaks of diseases like the Black Death, with significant social and economic impacts.
11. *Qing Dynasty*
The last imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912. The Qing Dynasty played a crucial role in shaping modern China, including its territorial expansion, economic policies, and relations with foreign powers.
12. *Quetzalcoatl*
A Mesoamerican deity worshipped by the Aztec, Toltec, and other civilizations. Quetzalcoatl, often depicted as a feathered serpent, was associated with wind, wisdom, and culture, and is central to understanding pre-Columbian religion and mythology.
13. *Qin Shi Huang*
The first emperor of a unified China, who ruled from 221 to 210 BCE. He is known for his centralizing reforms, the construction of the Great Wall, and his elaborate tomb guarded by the Terracotta Army, which is a major archaeological site.
14. *Quadrivium*
The four subjects of arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy, which formed part of the medieval liberal arts curriculum. The quadrivium, combined with the trivium, was essential in the education system of the Middle Ages.
15. *Quakerism*
A Christian movement that began in England in the 17th century, emphasizing simplicity, peace, and equality. The Quakers played an important role in social reform movements, including the abolition of slavery and women's rights, influencing modern history.
16. *Quipu Kamayoc*
A person trained in the use of quipu for record-keeping in the Inca Empire. These individuals were essential for managing taxes, census data, and other governmental records in Inca society.
17. *Quadrangular Castle*
A type of medieval fortification that features four corner towers and a rectangular layout. Quadrangular castles were common in Europe during the Middle Ages and are studied for their military architecture and feudal significance.
18. *Quoins*
Cornerstones or the external angle stones of buildings, especially in ancient architecture. Quoins are important for understanding building techniques and the structural integrity of ancient constructions.
19. *Quintessence*
In medieval philosophy and alchemy, quintessence referred to the fifth element, believed to be the pure essence of celestial bodies. While more philosophical than archaeological, it represents the worldview and scientific understanding of the time.
20. *Quasi-Feudalism*
A term used to describe societies that exhibit some features of feudalism without fully adhering to the European feudal model. Examples might include certain Asian or African civilizations that had hierarchical land tenure systems similar to European feudalism.
R
1. *Radiocarbon Dating*
A method used to determine the age of organic materials by measuring the decay of carbon-14. This technique is vital for dating archaeological finds from the last 50,000 years and is crucial for understanding timelines in prehistory.
2. *Romanesque Architecture*
A style of architecture prevalent in Europe during the 10th to 12th centuries, characterized by semi-circular arches, robust structure, thick walls, and large towers. It is important for studying medieval European religious and civic buildings.
3. *Renaissance*
A period of cultural, artistic, and intellectual revival in Europe, particularly from the 14th to the 17th century. The Renaissance marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and is key in understanding developments in art, science, and politics.
4. *Reconstruction*
In archaeology, the process of rebuilding or restoring ancient buildings, structures, or artifacts based on excavation data. It helps archaeologists and historians visualize ancient civilizations and their architectural achievements.
5. *Republic*
A form of government in which power is held by elected representatives rather than a monarch. The Roman Republic (509–27 BCE) is one of the most well-known historical examples, providing a model for modern democracies.
6. *Rococo*
An 18th-century artistic movement and style, especially in decorative arts, architecture, and painting, characterized by elaborate ornamentation and lightness. Rococo’s importance lies in its reflection of European aristocratic culture.
7. *Rosetta Stone*
An ancient Egyptian artifact discovered in 1799 that bears inscriptions in Greek, Demotic, and hieroglyphs. Its discovery allowed scholars to decipher Egyptian hieroglyphics, revolutionizing the study of ancient Egypt.
8. *Ritual*
Ceremonial acts performed in religious or social contexts. Archaeologists study ritual objects, architecture (such as temples), and burial practices to understand the belief systems and cultural values of ancient civilizations.
9. *Roman Empire*
A vast empire that ruled over much of Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East from 27 BCE to 476 CE (Western Empire). Its influence on law, architecture, language, and governance has shaped Western civilization.
10. *Remains*
The physical remnants of past human activity, including bones, artifacts, and structures. The analysis of remains is essential for reconstructing ancient lifeways, including diet, health, and social organization.
11. *Runes*
The alphabets used by ancient Germanic peoples, such as the Norse and Anglo-Saxons. Runes were often carved on stones, weapons, and monuments, providing valuable insights into the languages and beliefs of early European cultures.
12. *Relief*
A sculptural technique where the sculpted elements remain attached to a solid background of the same material. Reliefs, such as those found in ancient Egyptian and Mesopotamian art, are critical for interpreting religious and historical narratives.
13. *Repatriation*
The process of returning cultural artifacts or human remains to their country or people of origin. Repatriation is significant in archaeology and museum ethics, as it addresses historical injustices and the preservation of cultural heritage.
14. *Reformation*
A 16th-century religious movement that led to the creation of Protestantism and the decline of Catholic dominance in Europe. The Reformation profoundly impacted European politics, society, and intellectual life.
15. *Round Barrow*
A type of burial mound or tumulus, typically circular in shape, found across Europe. Round barrows are key archaeological features for studying burial practices, social structures, and religious beliefs in prehistoric societies.
16. *Romanization*
The process by which conquered peoples adopted Roman culture, language, and governance. Studying Romanization helps historians understand how the Roman Empire maintained control over vast and culturally diverse territories.
17. *Reliquary*
A container used to hold sacred relics, often associated with saints in Christianity. Reliquaries are important for the study of religious art and medieval church practices, as well as the role of relics in medieval European society.
18. *Radiometric Dating*
A broader category of dating techniques based on the decay of radioactive isotopes, including carbon-14. Radiometric dating methods, such as potassium-argon dating, are essential for dating ancient geological and archaeological samples.
19. *Renaissance Humanism*
An intellectual movement during the Renaissance that emphasized the study of classical texts and the value of human potential and achievements. Humanism played a key role in shaping modern European thought, art, and education.
20. *Rock Shelter*
A natural formation where ancient peoples sought shelter, leaving behind traces of habitation, such as tools, pottery, and rock art. Rock shelters are important archaeological sites for studying prehistoric human activity and adaptation to environments.
S
1. *Stratigraphy*
The study of rock layers (strata) and layering in archaeology. Stratigraphy is crucial for understanding the chronological sequence of human activities at a site, as older layers are typically deeper than newer ones.
2. *Sarcophagus*
A stone coffin, often elaborately decorated, used in ancient civilizations like Egypt, Greece, and Rome. Sarcophagi provide insights into burial practices, religious beliefs, and the status of individuals in ancient societies.
3. *Settlement*
A place where people establish a community. Archaeological excavations of settlements, from small villages to large urban centers, reveal information about daily life, social structures, and economic activities.
4. *Stele*
A stone or wooden slab, often inscribed or carved, used as a monument or marker. Stelae are significant for recording historical events, religious practices, and political decrees in ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians and Maya.
5. *Seriation*
A relative dating method used by archaeologists to arrange artifacts in a chronological sequence based on style or form. It helps establish the relative ages of objects when absolute dating methods are unavailable.
6. *Sumerians*
One of the earliest known civilizations, located in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), flourishing around 4500-1900 BCE. The Sumerians developed one of the earliest writing systems (cuneiform) and made advances in law, architecture, and agriculture.
7. *Sanctuary*
A sacred or holy place, often associated with temples or religious rituals. Sanctuaries in ancient cultures, such as those in Greece or Egypt, serve as key archaeological sites for understanding religious practices and beliefs.
8. *Scroll*
A rolled-up manuscript used in ancient times, typically written on materials like papyrus, parchment, or vellum. Scrolls, such as the Dead Sea Scrolls, are vital for studying ancient texts and religious writings.
9. *Sherd (or Shard)*
A fragment of pottery found at archaeological sites. Pottery sherds are often used to determine the age, function, and cultural context of a site, making them critical for archaeological interpretation.
10. *Silk Road*
A network of trade routes connecting China to the Mediterranean, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture. The Silk Road was crucial in spreading innovations, art, and religions across Asia, Europe, and Africa.
11. *Siege Warfare*
A method of attacking fortified structures, like castles or walled cities, by surrounding and cutting off supplies. Archaeological finds from siege sites, including weapons and fortifications, provide insights into military tactics and technologies.
12. *Seal*
An engraved object, usually in stone or metal, used to stamp an impression on wax, clay, or other materials to signify authenticity or ownership. Seals, particularly cylinder seals from Mesopotamia, offer insights into administrative and personal identity practices.
13. *Step Pyramid*
An ancient architectural form consisting of successively receding platforms. The most famous example is the Pyramid of Djoser in Egypt, one of the earliest monumental stone structures, marking the evolution of pyramid construction.
14. *Samurai*
The warrior class of feudal Japan, known for their military prowess and adherence to the code of Bushido. Samurai culture and artifacts, including swords and armor, are important for understanding Japan's medieval history.
15. *Sundial*
A device used to tell time by the position of the sun, casting a shadow on a calibrated surface. Ancient sundials reveal technological advancements and how time was understood and organized in historical societies.
16. *Synagogue*
A Jewish house of worship and communal gathering. Synagogues, along with their associated artifacts, provide insights into the religious and social life of Jewish communities in antiquity and the Middle Ages.
17. *Sword*
A bladed weapon used throughout history, often symbolizing military power and social status. The study of ancient swords, from the Bronze Age to medieval times, reveals technological innovations in metallurgy and warfare.
18. *Subaltern*
A term used in post-colonial studies to describe populations that are socially, politically, and geographically outside the dominant power structure. It is often used in historical analysis to examine the perspectives and experiences of marginalized groups.
19. *Stupa*
A dome-shaped structure used as a Buddhist shrine, often containing relics. Stupas are significant religious monuments, and their study offers insights into the spread of Buddhism and ancient architectural practices in Asia.
20. *Stratigraphic Excavation*
A method of excavation in archaeology where different layers of a site are carefully dug out in order to preserve the stratigraphic sequence. It helps in reconstructing the chronological order of human activities.
T
1. *Tumulus*
A mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli, also known as barrows, are common burial structures in many ancient cultures and provide insights into burial practices, status, and beliefs about the afterlife.
2. *Tell*
A type of archaeological mound created by human occupation over long periods, usually found in the Middle East. Tells are important for understanding the long-term habitation and cultural layers of ancient settlements.
3. *Terracotta*
A type of fired clay used in sculptures, pottery, and building materials. Terracotta figures and vessels, like those from the Terracotta Army in China, offer valuable information about ancient art, rituals, and technology.
4. *Tholos Tomb*
A beehive-shaped burial structure from the Mycenaean civilization in Greece, used between 1500-1200 BCE. Tholos tombs provide critical evidence of burial customs and social hierarchy in the ancient Aegean world.
5. *Textile*
Any cloth or woven fabric, often used in reference to historical and archaeological finds. The study of ancient textiles, including their materials and techniques, reveals much about trade, technology, and daily life in ancient societies.
6. *Temenos*
A sacred enclosure or precinct in ancient Greece and Rome, often surrounding a temple. Temenos spaces were used for religious purposes, and their study helps archaeologists understand ancient religious architecture and rituals.
7. *Torc*
A large rigid neck ring made of metal, worn as jewelry by ancient European peoples, especially the Celts. Torcs are significant artifacts for studying the wealth, craftsmanship, and social status of individuals in Iron Age Europe.
8. *Tribute*
A payment made by one state or ruler to another, often as a sign of submission or allegiance. Tributes were common in ancient empires, and their documentation is key for understanding the political relationships and economies of those times.
9. *Toga*
A garment worn by male Roman citizens, symbolizing Roman citizenship and social status. The toga is an important cultural symbol of ancient Rome, and its depictions in art help historians understand Roman social structures and values.
10. *Topography*
The study and mapping of the physical features of a place or region, especially in relation to historical or archaeological sites. Understanding topography is crucial for interpreting how ancient peoples used and interacted with their landscapes.
11. *Trilithon*
A structure consisting of two large vertical stones supporting a horizontal stone, often seen in megalithic monuments such as Stonehenge. Trilithons are studied for their architectural significance and religious or ceremonial purposes.
12. *Tribunal*
A type of court or governing body in ancient civilizations, such as those found in Roman or medieval contexts. The study of tribunals provides insights into ancient legal systems, justice, and political organization.
13. *Trowel*
A small hand tool used by archaeologists for careful digging and excavation. It is essential for precise work in uncovering artifacts and features during an excavation.
14. *Transhumance*
The seasonal movement of people with their livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. Archaeologists study transhumance patterns to understand ancient pastoralism and how communities adapted to their environments.
15. *Tabernacle*
A portable sanctuary used by the Israelites during the Exodus, as described in the Bible. The concept and reconstructions of tabernacles are important for understanding early religious architecture and worship practices in ancient Israel.
16. *Tithe*
A one-tenth portion of produce or earnings, paid as a contribution to support religious institutions. In medieval Europe, tithes were important for the economic support of churches and monasteries, and records of tithing provide insights into the economy and social obligations of the time.
17. *Trireme*
An ancient Greek or Roman warship, with three rows of oars on each side. Triremes were crucial in naval battles, and their study reveals important information about ancient maritime warfare and shipbuilding technology.
18. *Temple*
A structure dedicated to religious or spiritual activities, often serving as a house of worship for deities in ancient civilizations. Temples, such as the Parthenon in Greece or the Temples of Karnak in Egypt, are major archaeological sites for studying religious architecture and rituals.
19. *Tumulus Culture*
Refers to a prehistoric culture known for building burial mounds or barrows in Central Europe during the Bronze Age. The study of this culture's burial practices helps archaeologists understand the social and ritualistic behavior of the time.
20. *Tithe Barn*
A large barn used in medieval Europe to store tithes collected by the church, usually in the form of agricultural produce. These barns provide evidence of medieval ecclesiastical wealth, agricultural practices, and the role of the church in medieval economies.
U
1. *Urbanization*
The process by which rural areas develop into cities or towns. Archaeologists study urbanization by examining ancient settlements and the rise of cities to understand social, economic, and political developments.
2. *Ushabti*
Small funerary figurines placed in ancient Egyptian tombs, meant to serve the deceased in the afterlife by performing tasks on their behalf. Ushabtis offer insights into Egyptian beliefs about the afterlife and burial practices.
3. *Utopia*
An imagined perfect society, often discussed in historical philosophical texts, like Thomas More's Utopia (1516). Utopian ideas reflect historical critiques of existing societies and aspirations for ideal governance and social organization.
4. *Underworld*
In many ancient cultures, the underworld was a realm where the souls of the dead resided. Archaeological finds related to the underworld, such as burial rituals and tombs, provide clues about religious beliefs concerning death and the afterlife.
5. *Urn*
A vessel, typically made of ceramic, used to hold the remains of cremated individuals. Urn burials, found in cultures such as the ancient Romans and the Etruscans, provide important evidence for funerary customs.
6. *Upper Paleolithic*
The final phase of the Paleolithic era, dating from around 40,000 to 10,000 years ago, characterized by advanced stone tools and early forms of art, like cave paintings. This period marks significant developments in human culture and technology.
7. *Ubaid Culture*
An early Mesopotamian culture (circa 6500–3800 BCE), known for its distinct pottery and the first signs of urbanization in Southern Mesopotamia. The Ubaid period is important for understanding the precursors to later Mesopotamian civilizations, such as the Sumerians.
8. *Unifacial Tool*
A type of stone tool that has been flaked or worked on only one side. These tools are significant for understanding early human technological developments and subsistence strategies.
9. *Undercroft*
A vaulted space beneath a building, often used for storage or as a crypt in medieval structures. Undercrofts are important features in the study of medieval architecture and provide clues about the functional use of spaces in castles and churches.
10. *Urartu*
An ancient kingdom located in the region of modern-day Armenia, eastern Turkey, and northwestern Iran, flourishing from around 860 BCE to 590 BCE. The study of Urartian fortifications, inscriptions, and artifacts sheds light on the geopolitics of the ancient Near East.
11. *Uruk*
One of the first major cities in ancient Mesopotamia, considered one of the world's oldest cities (circa 4000 BCE). The archaeological study of Uruk reveals early urban planning, writing (cuneiform), and the development of monumental architecture.
12. *Usurper*
A person who seizes power unlawfully, often used in the context of rulers who take the throne by force. Usurpers are significant in the study of political history, as their actions often led to important changes in dynastic and governmental structures.
13. *Urban Archaeology*
The study of past cities and towns through their material remains, including buildings, streets, and artifacts. Urban archaeology focuses on understanding how people lived, worked, and interacted in densely populated areas.
14. *Utilitarianism*
A philosophical theory that suggests that actions are right if they are useful or benefit the majority. In historical studies, utilitarianism often influences interpretations of social policies and governance, particularly in the context of industrialization.
15. *Unstratified*
Refers to archaeological sites or layers where the stratigraphic sequence is unclear or has been disturbed. Unstratified contexts make it more difficult to determine the relative dating of artifacts and features.
16. *Uxorilocality*
A type of post-marital residence pattern where a married couple resides with or near the wife's family. Uxorilocality is studied in archaeology and anthropology to understand kinship and social organization in different cultures.
17. *Urartian*
Referring to the people, culture, and language of the ancient kingdom of Urartu. The Urartians are known for their advanced irrigation systems, metallurgy, and fortifications, which provide significant insights into early state formation in the Near East.
18. *Unicorn*
A mythical creature often depicted in medieval art and texts. While unicorns are not real, their symbolism in history reflects societal values, religious beliefs, and mythologies that are important to understanding medieval thought and literature.
19. *Umbra*
Refers to the shadow or darkened area, often used in the context of solar eclipses. In history, the study of astronomical events like eclipses has helped archaeologists and historians date specific events and understand ancient scientific knowledge.
20. *Urnfield Culture*
A late Bronze Age culture in central Europe (circa 1300-750 BCE), named for its burial practice of placing cremated remains in urns and burying them in fields. The Urnfield Culture is significant for understanding the transition between the Bronze and Iron Ages in Europe.
V
Vault
An architectural feature that forms a roof or ceiling with an arched or curved structure, commonly used in ancient Roman and medieval buildings. Vaults are significant for understanding architectural advancements and structural techniques.
Votive Offering
Objects or materials given as a devotional act to a deity or in gratitude for divine intervention. Votive offerings, such as figurines, inscriptions, or pottery, provide insights into religious practices and beliefs in ancient cultures.
Vestige
A trace or remnant of something that was once present. In archaeology, vestiges include fragments of buildings, artifacts, or inscriptions that help reconstruct historical sites and understand past societies.
Vernacular Architecture
The traditional architectural styles and techniques used by local communities, often reflecting regional materials and cultural practices. Studying vernacular architecture provides insights into the daily lives and environmental adaptations of historical populations.
Villanovan Culture
An Iron Age culture in Italy (circa 900-700 BCE), considered the precursor to Etruscan civilization. Villanovan artifacts, such as cremation urns and metalwork, offer valuable information about early Italic societies.
Vicus
A term used to describe a small Roman settlement or village, often situated near larger cities. Vicus sites provide insights into rural life and the organization of Roman provincial towns.
Vassal
A person or state that holds land from a feudal lord in exchange for military service or other obligations. The study of vassal relationships helps historians understand feudal systems and medieval political structures.
Varna
A site in Bulgaria known for its extensive and well-preserved burial mounds dating to the Copper Age (circa 4600–4200 BCE). The Varna Necropolis is significant for its rich grave goods and insights into early social stratification and metallurgy.
Venus Figurines
Small prehistoric sculptures of female figures, often associated with fertility and the Paleolithic era. Venus figurines, such as the Venus of Willendorf, provide evidence of early symbolic and artistic expression.
Votive Tablet
A small, inscribed tablet used as an offering to a deity or to record a votive dedication. Votive tablets often contain inscriptions detailing the purpose of the offering and are valuable for understanding religious practices.
Vestibule
An entrance hall or space leading into a building, commonly found in Roman and medieval architecture. The vestibule’s design and use offer insights into the spatial organization and ceremonial functions of ancient structures.
Viking Age
The period from the late 8th to the early 11th century, during which Norse seafarers, known as Vikings, explored, raided, and settled across Europe. Viking Age artifacts, such as runestones and ship remains, shed light on Norse culture and expansion.
Votive Statue
A statue dedicated to a deity as a votive offering. Votive statues, often found in temples, provide information about religious devotion, artistic styles, and the status of individuals in ancient societies.
Vassalage
The system of relationships and obligations between a lord and his vassals in the feudal system. Vassalage helps historians understand medieval social hierarchies and land ownership structures.
Votive Relief
A sculpted stone relief dedicated to a deity as a votive offering. Votive reliefs often depict scenes of worship or gratitude and are important for studying religious practices and artistic techniques.
Vicus
A Roman term for a small rural settlement or village. Study of vicus sites helps in understanding the distribution of Roman settlements and their integration into the larger Roman economy.
Vulcanization
A chemical process for treating rubber to make it more durable, developed in the 19th century. While not ancient, the study of vulcanization is relevant for understanding technological advancements in historical contexts.
Vellum
A fine-quality writing material made from animal skin, used in ancient manuscripts and documents. Vellum manuscripts provide valuable information about historical texts, calligraphy, and book production methods.
Viking Longship
A type of ship used by the Vikings, characterized by its long, narrow design and shallow draft, ideal for raiding and exploration. Longships are significant for understanding Viking maritime technology and expansion.
Votive Inscription
An inscription dedicated as a votive offering to a deity, often found on stone tablets or altars. Votive inscriptions provide details about religious practices, dedications, and the social status of individuals in ancient cultures.
W
1. *Wadi*
A dry riverbed or valley in arid regions that temporarily fills with water during rain. Studying wadis helps archaeologists understand ancient water management and settlement patterns in desert environments.
2. *Wall*
A vertical structure that encloses or divides an area, often found in fortifications, cities, and buildings. Walls provide evidence of ancient defensive architecture, urban planning, and social organization.
3. *Wattle and Daub*
A construction technique using woven wooden branches (wattle) covered with a mixture of clay and straw (daub). This method, used in various ancient cultures, helps archaeologists reconstruct early domestic architecture.
4. *Wheat*
A staple crop cultivated since ancient times, with archaeological evidence of its domestication and cultivation. Studying ancient wheat remains provides insights into agricultural practices and diet in historical societies.
5. *Workshop*
A place where artisans or craftsmen produced goods, such as pottery or metalwork. Excavations of ancient workshops reveal information about technology, trade, and daily life.
6. *Wagon*
A wheeled vehicle used for transport, often drawn by animals. Ancient wagons are significant for understanding trade, mobility, and technological advancements in transportation.
7. *Wooden Artifact*
Objects made from wood, such as tools, weapons, or furniture. Wooden artifacts, which often require special preservation techniques, provide valuable information about ancient craftsmanship and daily life.
8. *Writing System*
A method of recording language through symbols or characters, such as cuneiform or hieroglyphics. The study of writing systems is crucial for understanding ancient communication, administration, and culture.
9. *Watershed*
The area of land where all water drains into a particular river or body of water. Archaeologists study watersheds to understand ancient water management systems and settlement patterns.
10. *Wadi-Supported Settlement*
Settlements established in wadis or dry riverbeds where water was temporarily available. These settlements provide evidence of how ancient peoples adapted to arid environments.
11. *Writings*
Recorded texts from ancient cultures, including literature, administrative records, and inscriptions. Historical writings are essential for reconstructing historical events, ideologies, and daily life.
12. *Walled City*
A city enclosed by defensive walls, often found in ancient civilizations. The study of walled cities helps archaeologists understand urban planning, defense strategies, and societal organization.
13. *Warfare*
The practice of armed conflict between societies or states. Archaeological evidence of warfare, such as weapons and fortifications, provides insights into ancient military tactics and conflicts.
14. *Watermill*
A device that uses flowing water to power machinery, such as grinding grain. Watermills, found in various ancient cultures, illustrate advancements in technology and changes in agricultural practices.
15. *Whorl*
A type of ancient spindle or textile tool with a circular shape, used for spinning fibers into thread. Whorls help archaeologists understand textile production techniques and economic activities.
16. *Warfare Archaeology*
The study of material remains related to armed conflict, such as fortifications, weapons, and battlefield sites. Warfare archaeology provides insights into military strategies, technology, and the impact of conflict on societies.
17. *Wine Press*
A device used to extract juice from grapes for winemaking. Ancient wine presses reveal information about viticulture, trade, and social practices related to wine consumption.
18. *Wagon Train*
A group of wagons traveling together, often for trade or migration purposes. Wagon trains are important for understanding patterns of migration, trade routes, and the movement of people.
19. *Warrior*
A person engaged in combat or warfare, often depicted in historical and archaeological records. The study of warriors and their artifacts helps historians understand social roles, military practices, and conflict.
20. *Wheel*
A round object that rotates around an axle, used in various ancient technologies, including carts and chariots. The invention and use of wheels represent a significant advancement in transportation and technology.
X
1. *Xenophon*
An ancient Greek historian and soldier who wrote "Anabasis," detailing his experiences with the Ten Thousand, a Greek mercenary army. Xenophon's works are valuable for understanding Greek military history and the Persian Empire.
2. *Xerxes I*
A Persian king known for his invasion of Greece during the Greco-Persian Wars (480 BCE). Xerxes' reign and military campaigns are significant for studying ancient Persian history and its interactions with Greece.
3. *Xerography*
A method of copying documents using electrostatic charges, developed in the 20th century. While not ancient, the term is relevant for understanding the evolution of document reproduction techniques.
4. *Xylography*
The art of engraving on wood, often used for printing. Xylography provides insights into early printing techniques and the production of illustrated texts.
5. *Xenocentric*
A perspective that views other cultures or societies as superior to one's own. Xenocentric viewpoints are studied in historical and archaeological contexts to understand intercultural relations and biases.
6. *Xenolith*
A fragment of rock trapped within another rock, often found in volcanic regions. Xenoliths can provide information about the geological history and the formation of ancient landscapes.
7. *Xylophone*
A musical instrument made of wooden bars struck by mallets. While not directly related to ancient history, ancient xylophones and similar instruments provide insights into musical practices and cultural traditions.
8. *Xenoclasm*
The destruction or vandalism of objects or monuments from foreign cultures, often as a form of cultural or ideological opposition. Xenoclasm is relevant for studying conflicts and cultural interactions in history.
9. *Xenodochium*
A medieval institution for hosting and caring for travelers and pilgrims, often associated with monasteries. Xenodochia offer insights into medieval hospitality practices and religious institutions.
10. *Xerxes' Inscriptions*
Epigraphic evidence from the reign of Xerxes I, including the famous Behistun Inscription, which provides details about Persian royal propaganda and administrative practices.
11. *Xystus*
An open courtyard or garden, often found in Roman architecture. Xystus areas provide information about Roman domestic architecture and leisure spaces.
12. *Xenia*
The Greek concept of hospitality and the relationship between hosts and guests. The study of xenia helps historians understand social customs, diplomacy, and cultural exchanges in ancient Greece.
13. *Xenagoras*
An ancient Greek historian and writer known for his accounts of the Persian Empire and its interactions with Greece. His works contribute to the understanding of ancient Near Eastern history.
14. *Xeriscaping*
A landscaping method designed to reduce water usage, often applied in arid regions. While modern, the study of xeriscaping techniques can provide insights into historical water management practices.
15. *Xenon*
A chemical element used in modern archaeology for certain dating methods, such as dating ancient ice cores. The term is relevant for understanding the scientific techniques used in archaeological dating.
16. *Xenogenesis*
The concept of producing offspring that are significantly different from their parents, a term more commonly used in biology. In historical contexts, it can metaphorically describe cultural or social changes.
17. *Xylotomy*
The study and preparation of thin sections of wood for microscopic examination. Xylotomy helps in understanding ancient wood usage and the preservation of wooden artifacts.
18. *Xenon Dating*
A modern scientific method for dating geological and archaeological samples using the radioactive decay of xenon isotopes. This technique provides precise dating for ancient materials.
19. *Xylorimba*
A type of xylophone with a marimba-like sound. Ancient versions or similar instruments provide insights into the musical traditions and cultural practices of historical societies.
20. *Xiphos*
A type of ancient Greek short sword used by hoplites and other soldiers. The study of xiphos and related weaponry provides insights into Greek warfare and military equipment.
Y
1. *Yarn*
Thread made from fibers, often used in ancient textile production. Archaeologists study yarn remnants to understand ancient weaving techniques and textile technologies.
2. *Yuan Dynasty*
The Chinese dynasty founded by Kublai Khan that ruled from 1271 to 1368 CE. The Yuan Dynasty is significant for its impact on Chinese history, trade, and cultural exchanges during the Mongol Empire.
3. *Yam*
A tuberous root vegetable cultivated in ancient agricultural societies. Archaeological finds of yam cultivation provide insights into ancient diet and agricultural practices.
4. *Yuga*
In Hindu cosmology, a Yuga is an epoch or era within a cycle of ages. Understanding Yugas helps historians and archaeologists place historical events and cultural developments within a broader temporal framework.
5. *Yew Tree*
A type of evergreen tree used in ancient times for making bows and ceremonial objects. The study of yew wood artifacts provides information about ancient weaponry and ritual practices.
6. *Yarmulke*
A small cap worn by Jewish men, especially during religious practices. While not ancient, the study of yarmulkes and their historical evolution provides insights into religious attire and cultural practices.
7. *Yasak*
A term used in Ottoman history referring to a tax or tribute. Yasak records help historians understand the economic and administrative aspects of the Ottoman Empire.
8. *Ypres*
A Belgian city known for its significant battles during World War I, including the Battle of Ypres. Studying the Ypres battles provides insights into World War I military strategies and the impact of warfare on urban centers.
9. *Yuanmingyuan (Old Summer Palace)*
An imperial garden and palace complex in Beijing, China, destroyed during the Second Opium War (1860). The study of Yuanmingyuan's ruins offers insights into Qing Dynasty architecture and cultural heritage.
10. *Yamen*
A traditional Chinese administrative office or residence of a local official. Archaeological studies of yamen structures provide insights into historical governance and local administration in China.
11. *Yohimbine*
A compound derived from the bark of the yohimbe tree, used in ancient African medicine. The study of yohimbine provides insights into traditional medicine and herbal practices in historical contexts.
12. *Yarmuk River*
A river in the Middle East that marked the boundary between the Byzantine Empire and the early Islamic Caliphates. The Battle of Yarmuk (636 CE) was significant in the expansion of the Islamic Empire.
13. *Yazidism*
A religious tradition originating in the Middle East, practiced by the Yazidi people. The study of Yazidism helps historians understand the religious and cultural diversity of the region.
14. *Yamato Period*
The period in Japanese history from the 3rd to the 7th century CE, characterized by the consolidation of early Japanese states. Artifacts from the Yamato period provide insights into early Japanese political and cultural developments.
15. *Ypres Salient*
A bulge in the front line of the Western Front during World War I, where significant battles occurred. The Ypres Salient is crucial for understanding trench warfare and its impact on the battlefield.
16. *Yoni*
A symbol in Hinduism representing the goddess Shakti and the female reproductive system. Yoni artifacts and symbols are studied to understand ancient religious practices and iconography.
17. *Yukon*
A region in North America known for its Klondike Gold Rush in the late 19th century. The study of Yukon’s mining history provides insights into the impact of gold rushes on migration and economic development.
18. *Yugas*
Cyclical epochs in Hindu cosmology, including the Satya Yuga, Treta Yuga, Dvapara Yuga, and Kali Yuga. The concept of Yugas is important for understanding Hindu historical and cultural frameworks.
19. *Yishuv*
The Jewish community in Palestine before the establishment of the State of Israel. Studying the Yishuv provides insights into the development of Jewish settlement and socio-political movements in the region.
20. *Yersinia pestis*
The bacterium responsible for the Black Death or Bubonic Plague. Archaeological studies of Yersinia pestis help understand the impact of pandemics on historical populations and societies.
Z
1. *Ziggurat*
A massive terraced structure built in ancient Mesopotamia, often serving as a temple complex. Ziggurats, such as the Ziggurat of Ur, are crucial for understanding Mesopotamian religious practices and architectural advancements.
2. *Zeus*
The chief deity in ancient Greek mythology, often depicted as the ruler of Mount Olympus. Artifacts and texts related to Zeus provide insights into ancient Greek religion, mythology, and cultural practices.
3. *Zenith*
The highest point reached by a celestial body in the sky. In archaeology, understanding the zenith helps in studying ancient astronomical practices and alignments in structures like observatories or pyramids.
4. *Zhou Dynasty*
An ancient Chinese dynasty that ruled from approximately 1046 to 256 BCE. The Zhou Dynasty is significant for its contributions to Chinese philosophy, governance, and culture.
5. *Zoroastrianism*
One of the world's oldest monotheistic religions founded by the prophet Zoroaster in ancient Persia. Zoroastrian texts and artifacts offer valuable insights into early religious beliefs and practices in ancient Iran.
6. *Ziggurat of Ur*
A well-preserved example of a ziggurat located in modern-day Iraq, dating back to the early 21st century BCE. The Ziggurat of Ur provides important information about Sumerian architecture and religious practices.
7. *Zeno of Elea*
An ancient Greek philosopher known for his paradoxes. While not directly related to material archaeology, his philosophical ideas influence historical understanding of ancient Greek thought and logic.
8. *Zanj*
A term used to refer to the East African coast or the people from this region, particularly during the medieval period. The study of Zanj helps understand trade networks and cultural exchanges between Africa and the Arabian Peninsula.
9. *Zarathustra*
Another name for the founder of Zoroastrianism, also known as Zoroaster. His teachings and influence are important for understanding the development of religious and philosophical ideas in ancient Persia.
10. *Zama*
The site of the Battle of Zama in 202 BCE, where Scipio Africanus defeated Hannibal of Carthage. The battle was a decisive moment in the Second Punic War and has significant implications for the history of Rome and Carthage.
11. *Zettabyte*
A unit of digital information equal to one sextillion bytes. While modern, understanding data storage and management is relevant for historical research involving large-scale digital archives and databases.
12. *Zürich*
A city in Switzerland with significant historical importance, particularly during the Reformation. Studying Zurich’s role provides insights into religious and political changes in Europe during the 16th century.
13. *Ziggurat of Chogha Zanbil*
An ancient Elamite ziggurat in modern-day Iran, built around 1250 BCE. The site is important for understanding the architectural and religious practices of the Elamite civilization.
14. *Zen*
A school of Mahayana Buddhism that originated in China and emphasizes meditation. Zen’s influence on East Asian culture, art, and philosophy is significant in historical and archaeological studies.
15. *Zoroastrian Fire Temple*
A place of worship for Zoroastrians, where sacred fires are maintained. The study of fire temples provides insights into Zoroastrian religious practices and architectural styles.
16. *Zygomatic Arch*
A bony structure in the skull forming the prominence of the cheek. The zygomatic arch is important in anthropological and archaeological studies for reconstructing the appearance of ancient human populations.
17. *Zaidis*
A sect of Shia Islam that emerged in the 8th century CE. The study of Zaidi practices and history provides insights into Islamic sects and their development in early Islamic history.
18. *Zhoukoudian*
An archaeological site in China famous for the discovery of Peking Man, an early hominid. Zhoukoudian provides crucial evidence about human evolution and early human habitation in East Asia.
19. *Zaman*
A term used in various historical contexts to denote periods or ages. Understanding the concept of zaman helps in categorizing and analyzing historical periods and developments.
20. *Zacatecas*
A historical city in Mexico known for its rich mining history and colonial architecture. Studying Zacatecas offers insights into the impact of mining on colonial societies and the development of Spanish America.
*About the Author*
Lalit Mohan Shukla, a distinguished scholar and writer, has made a significant impact across multiple fields through his best-selling books and widely appreciated e-books. Among his prominent works are Motivational Poetry by Lalit Mohan Shukla, Handbook of Science Terminology, and Handbook of Forestry Terminology. He has also published a variety of successful e-books on Amazon KDP, including Global Science Today: Unveiling the Frontiers of Innovation, E-books: Competitive Edge, Nanotechnology Unveiled: Exploring Benefits, Applications, and Essential Precautions, Handbook for AI, IT, and Blogging Terminology, and Handbook for Sports Terminology.
His literary contributions also extend to motivational and educational guides such as Life’s Inspiring Words: Empowering Quotes for Everyday Strength and Motivation and Managing Excellence School: A Guide for Educators. His latest book, Handbook of English Language and Literature, reflects his deep expertise in the field.
In addition to his written works, Mr. Shukla is a globally acclaimed blog writer, with his blog https://getinspirebylalit.blogspot.com gaining wide viewership and recognition from readers around the world.
Academically, Lalit Mohan Shukla holds a graduate degree in Science and postgraduate degrees in three key disciplines—Ancient Indian History, Culture, and Archaeology; English Literature; and Education. He further holds an M.Phil. in Ancient Indian History, Culture, and Archaeology. His educational background, coupled with his strong language teaching skills, has greatly benefited professionals in many fields.






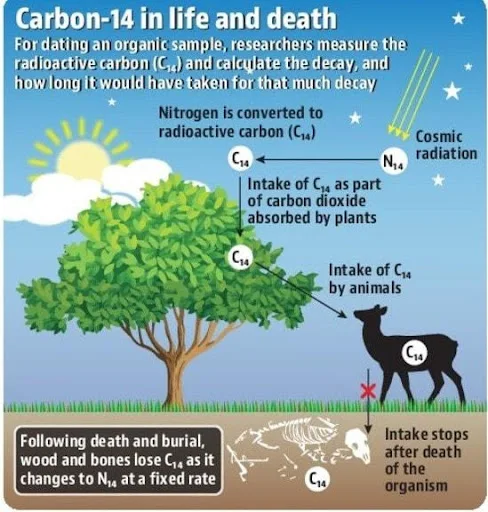







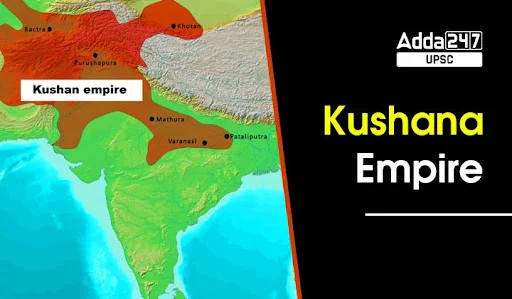






















No comments:
Post a Comment
thank you